
Breaking News
 US Deploys F-22 Fighter Jets to Southern Israel as Massive Military Buildup Continues
US Deploys F-22 Fighter Jets to Southern Israel as Massive Military Buildup Continues
 Elon Musk 'Legacy media lies relentlessly' from clip: It is the media that is racist'
Elon Musk 'Legacy media lies relentlessly' from clip: It is the media that is racist'
 Zohran Mamdani forces cops to pray to Allah (2nd clip) – He and AOC announce free health care...
Zohran Mamdani forces cops to pray to Allah (2nd clip) – He and AOC announce free health care...
 Why Can't We Thrive Like 1905?
Why Can't We Thrive Like 1905?
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Metallic Wood: New Material That Is As Strong As Titanium But 5 Times Lighter
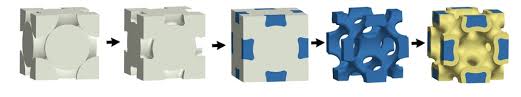
Although it's not a new element and basically consists of nickel, it is four to five times lighter than titanium thanks to its unique porous construction which is similar to natural materials such as wood: hence the name Metallic Wood.
The study was led by James Pikul, Assistant Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics at Penn Engineering. Here is what he had to say about this material:
The reason we call it metallic wood is not just its density, which is about that of wood, but its cellular nature. Cellular materials are porous; if you look at wood grain, that's what you're seeing — parts that are thick and dense and made to hold the structure, and parts that are porous and made to support biological functions, like transport to and from cells.
Our structure is similar. We have areas that are thick and dense with strong metal struts, and areas that are porous with air gaps. We're just operating at the length scales where the strength of struts approaches the theoretical maximum.



