
Breaking News
 Full-Out, Digitized Technocratic Rule Is Not Around The Corner, It Is Next Door
Full-Out, Digitized Technocratic Rule Is Not Around The Corner, It Is Next Door
 Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
 Hormuz Is Closing -- Oil Skyrockets. Food and Chips Are Next...
Hormuz Is Closing -- Oil Skyrockets. Food and Chips Are Next...
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Cell division recreated outside of a cell for the first time
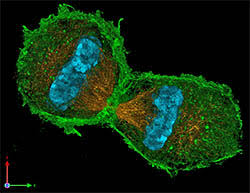
From the time we're conceived as just a single cell, to our wounds healing themselves in adulthood, cell division is a key part of how living organisms grow and survive. While we understand how this works on the broad scale, the nuances are still somewhat lost on us.
So the researchers on the new study set out to investigate the process further. To do so, they removed the "ingredients" from a cell and reconstructed them outside. But what they didn't expect was that this makeshift cell would undergo division like a normal cell.
First the team separated out actin, a protein that's key to the cellular division process. The actin proteins, which are long and rod-shaped, tended to clump together in parallel lines, forming a kind of almond-shaped droplet.
The real magic happened when the researchers added myosin, a motor protein that plays a part in muscle contraction. Surprisingly, the myosin moved towards the center of the actin droplets, then pinched them off from the middle, forming two separate "cells."

 Going Down with the Ship
Going Down with the Ship


