
Breaking News
 Full-Out, Digitized Technocratic Rule Is Not Around The Corner, It Is Next Door
Full-Out, Digitized Technocratic Rule Is Not Around The Corner, It Is Next Door
 Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
 Hormuz Is Closing -- Oil Skyrockets. Food and Chips Are Next...
Hormuz Is Closing -- Oil Skyrockets. Food and Chips Are Next...
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
MIT study identifies dynamic drug duo that's surprisingly effective against cancer
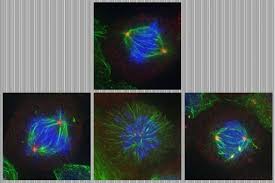
Now researchers at MIT have identified a surprising new dynamic drug duo, combining two classes that are already beginning to be widely used. Interestingly, the combo appears to work in a completely different way to what scientists previously expected.
The researchers started with a class of drugs called PLK1 inhibitors, which have proven effective in the past and are beginning to be tested in phase 2 clinical trials. The team set out to boost the effects of this type of drug, to see if it could be made even more effective.
PLK1 inhibitors primarily work by messing with mitosis, the process cancer cells use to divide and spread quickly. But as a side effect, they can also cause oxidative damage to cells – and this is the area the team wanted to give a leg up to. The researchers reasoned that PLK1 inhibitors could be even more potent a cancer-killer if they paired them up with another drug that prevents cells from repairing oxidative damage.

 Going Down with the Ship
Going Down with the Ship


