
Breaking News
Importing Poverty into America: Devolving Our Nation into Stupid
 Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
 Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
 The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Single thin lens able to focus the entire visible spectrum...
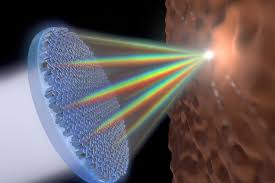
This has only ever been achieved in conventional lenses by stacking multiple lenses.
* Metalenses are thin, easy to fabricate and cost-effective. This breakthrough extends those advantages across the whole visible range of light. This is the next big step.
Metalenses — flat surfaces that use nanostructures to focus light — promise to revolutionize optics by replacing the bulky, curved lenses currently used in optical devices with a simple, flat surface. But, these metalenses have remained limited in the spectrum of light they can focus well.
Focusing the entire visible spectrum and white light – combination of all the colors of the spectrum — is so challenging because each wavelength moves through materials at different speeds. Red wavelengths, for example, will move through glass faster than the blue, so the two colors will reach the same location at different times resulting in different foci. This creates image distortions known as chromatic aberrations.



