
Breaking News
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 FBI Obtains Election Records From Arizona Senate
FBI Obtains Election Records From Arizona Senate
 While COMEX slept, tokenized gold revealed a signal
While COMEX slept, tokenized gold revealed a signal
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Alzheimer's hope as scientists find a way to stop the build-up of plaques in the brain that are.
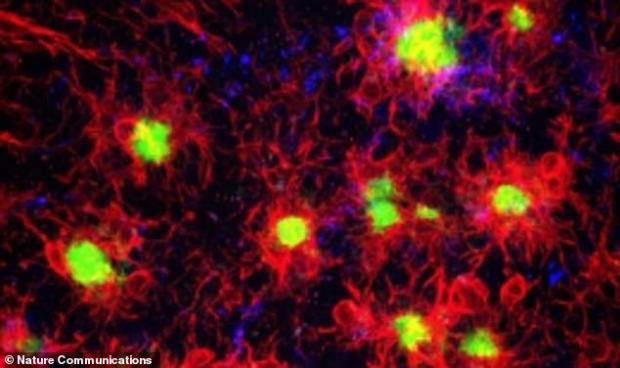
Scientists claim to have discovered a way to stop the build-up of a toxic protein in the brain that is considered to be a tell-tale sign of Alzheimer's.
Amyloid β protein has repeatedly been found to clog the brains of patients with the memory-robbing disorder, poisoning and killing crucial cells.
Researchers removed immune cells called microglia from the brains of mice with signs of Alzheimer's – studies have shown the cells 'turn on' genes for the disease.
Once the microglia were removed, the mice did not develop the hallmark amyloid β plaques. The team described the results of their study as 'striking'.
The researchers at the University of California, Irvine, hope their study will lead to new treatments that 'affect microglia in targeted ways'.
Dementia affects 850,000 people in the UK, of which 62 per cent have Alzheimer's, the most common form of the disease, according to the Alzheimer's Society.



