
Breaking News
 EXCLUSIVE: "The HUGE Elephant In The Room Is Actually What Jeffrey Epstein Was Best At..."
EXCLUSIVE: "The HUGE Elephant In The Room Is Actually What Jeffrey Epstein Was Best At..."
 EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW: Republican Candidate For Texas Governor "Doc" Pete Chambers Joins...
EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW: Republican Candidate For Texas Governor "Doc" Pete Chambers Joins...
 Epstein Files Trigger Political Fallout Across Europe
Epstein Files Trigger Political Fallout Across Europe
 Conjoined twin 'influencers' who have gained more than 280,000 followers with their intimate
Conjoined twin 'influencers' who have gained more than 280,000 followers with their intimate
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
'First of its Kind' Zero-Emission Geothermal Energy System in Canada May Soon Be in Your Tow
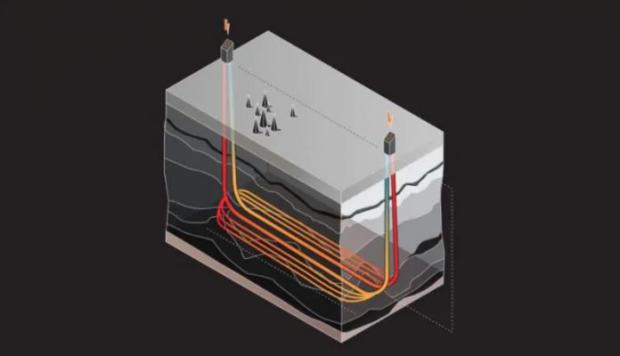
The Eavor Loop is a scalable closed-loop system that could soon allow us to generate consistent, unlimited electricity from the heat emanating from the Earth's core.
The system works like a radiator. The Eavor Loop consists of two wells that are drilled about 2 miles deep (3.5 kilometers) and 3 miles apart (5 kilometers) with several connecting pipes between the two. The wells then circulate proprietary fluid through the loop in order to absorb the Earth's heat and use it to make electricity.
The closed-loop design means that—unlike other geothermal projects—the system requires no fracking or water; it generates zero greenhouse gas emissions; it doesn't run the risk of polluting nearby water sources; and unlike wind or solar power, it does not depend on external elements to generate electricity.
"It's just a much more benign system and it's something that you can implement across 80% of the world instead of 5% of the world like traditional geothermal," Eavor Technologies CEO and President John Redfern told CBC News.
"You can put it almost anywhere. It's not like a windmill or solar panel … almost everything's underground so you can literally put it in someone's backyard."
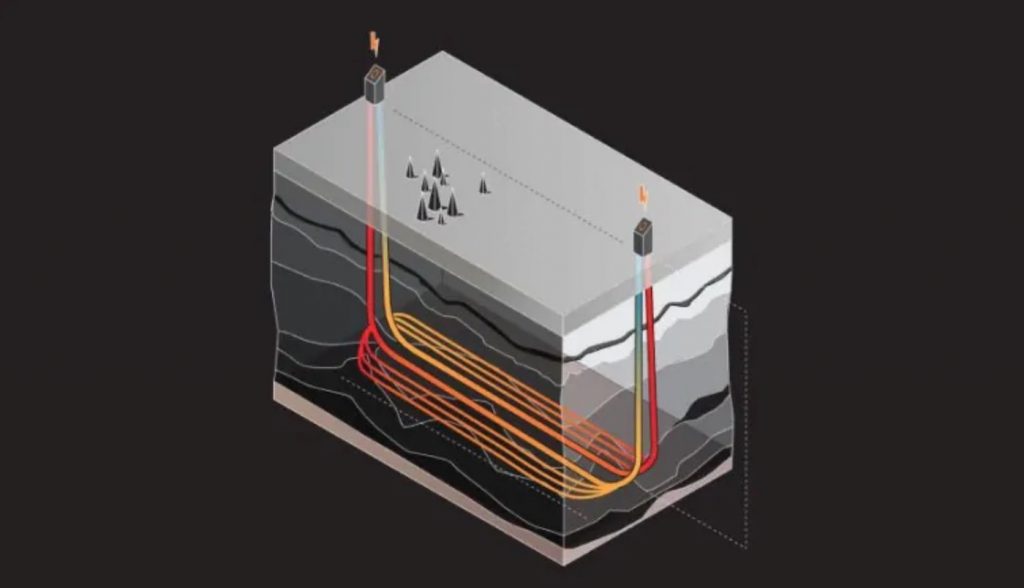
Photo by Eavor Technologies Inc.
Eavor Technologies recently began construction on a new $10 million testing facility in Alberta. With the first-of-its-kind pilot project expected to conclude by the end of the year, government representatives have helped to fund the project with the hopes that it will provide new jobs for regional oil and gas workers who may want to transition into the green energy sector.



