
Breaking News
 The Federal Reserve is planned to inject $16 billion into the economy this week...
The Federal Reserve is planned to inject $16 billion into the economy this week...
 Dr. Rhonda Patrick: Fasting, Creatine, Brain Performance & Longevity Breakthroughs | PBD #740
Dr. Rhonda Patrick: Fasting, Creatine, Brain Performance & Longevity Breakthroughs | PBD #740
 HIGH ALERT! Americans Will Die for Israel's Evil War with Iran | Redacted w Clayton Morris
HIGH ALERT! Americans Will Die for Israel's Evil War with Iran | Redacted w Clayton Morris
 The BEST Natural Dewormer for Sheep & Goats (That Actually Works)
The BEST Natural Dewormer for Sheep & Goats (That Actually Works)
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Antibiotics given to 80% of premature babies may alter their gut bacteria for DECADES...
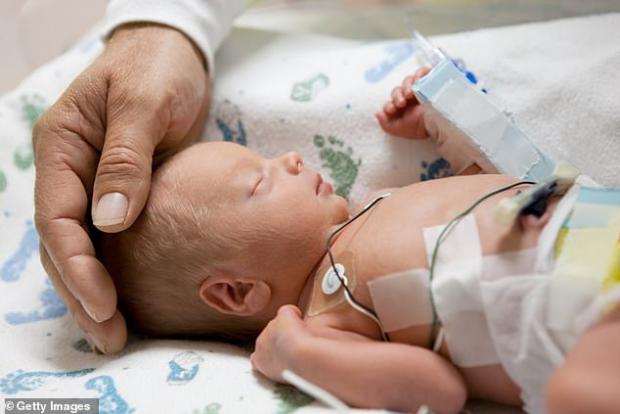
Most premature babies - about 80 percent - are given antibiotics in their first weeks of life to protect them from potentially fatal bacterial infections.
However, receiving this treatment for several months - even after they leave the NICU - may permanently alter their gut bacteria, a new study finds.
Compared to babies that weren't given antibiotics, the microbiomes of preemies had not only less diverse bacteria, but also more bacteria linked to antibiotic-resistance.
The team, from Washington University in St Louis School of Medicine, says its findings suggest that neonatologists should reduce their use of antibiotics in premature babies from a few months to just a few weeks.
'The immune system is pretty much set by age three,' senior author Dr Gautam Dantas, a professor of pathology and immunology at Washington University, told DailyMail.com.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

