
Breaking News
 Is Silver Going Back Below $50? Here's What the Data Suggests
Is Silver Going Back Below $50? Here's What the Data Suggests
 The Iran Deception, With Guest Dr. Matt Rostami
The Iran Deception, With Guest Dr. Matt Rostami
 EXCLUSIVE: General Flynn Issues An Emergency Warning To President Trump
EXCLUSIVE: General Flynn Issues An Emergency Warning To President Trump
 Trump Becomes the Glyphosate President: Declares Deadly Weed Killer Herbicide...
Trump Becomes the Glyphosate President: Declares Deadly Weed Killer Herbicide...
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Magnetic resonance imaging of melanoma exosomes
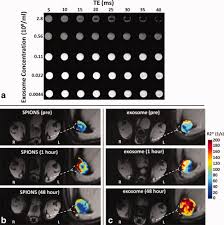
The ability to modify and track exosomes in vivo is essential to understanding exosome pathogenesis, and for utilizing exosomes as effective diagnostic and therapeutic nanocarriers to treat diseases.
Researchers from the Washington University School of Medicine recently reported a new electroporation method that allow exosomes to be loaded with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance tracking. Building on this approach, they now demonstrate for the first time using a C57BL/6 mouse model that melanoma exosomes can be imaged in vitro, and within lymph nodes in vivo with the use of standard MRI approaches.



