
Breaking News
 4409 -- How Christians were Hoodwinked by the Scofield Bible
4409 -- How Christians were Hoodwinked by the Scofield Bible
Why Do They Hate Thomas Massie
 3 MILLION Epstein Pages Released - I Can't Unsee What I Found
3 MILLION Epstein Pages Released - I Can't Unsee What I Found
 David Morgan and Mike Adams Talk Silver Demand, Refinery Shortages,...
David Morgan and Mike Adams Talk Silver Demand, Refinery Shortages,...
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
IPFS Browser Update
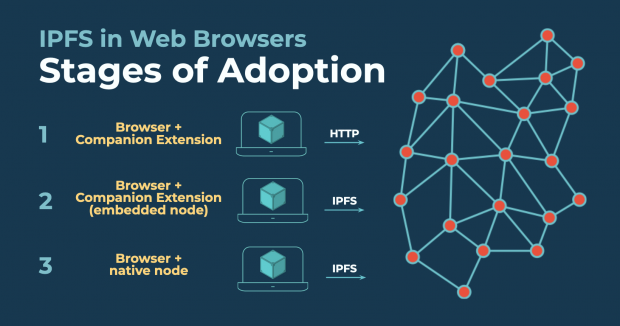
Right now, software that is fully in the control of the user is often too technical, too fragile, and too time-consuming to be the default choice.
But we're making headway. Today, we'd like to share some collaborations the IPFS project has had in the works for a while, which bring us a few steps closer to making unmediated access to information just work… by solving that "last mile" problem and integrating IPFS directly into web browsers.
The path to a truly decentralized web is a long one. For over 30 years the browser has been a client – but a foundational concept in P2P systems is that a participant is both a client and a server. Web browser vendors and web standards bodies have not designed for this architectural shift, so we're breaking it down into steps.
From the beginning, IPFS had an HTTP gateway. The gateway lets HTTP clients like web browsers publish to and read from the IPFS network. Now there are lots of different public HTTP gateways to the IPFS network, and the gateway we run at ipfs.io serves over five million requests per day.



