
Breaking News
 BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
 The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
 Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
 Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Researchers at Cardiff University have discovered a new type of killer T-cell that offers hope of a
T-cell therapies for cancer—where immune cells are removed, modified and returned to the patient's blood to seek and destroy cancer cells—are the latest paradigm in cancer treatments.
The most widely-used therapy, known as CAR-T, is personalized to each patient, but it only targets a few types of cancers and has not been successful for solid tumors, which make up the vast majority of cancers.
Cardiff researchers have now discovered T-cells equipped with a new type of T-cell receptor (TCR) which recognizes and kills most human cancer types, while ignoring healthy cells.
This TCR recognizes a molecule present on the surface of a wide range of cancer cells as well as in many of the body's normal cells but, remarkably, is able to distinguish between healthy cells and cancerous ones, killing only the latter.
The researchers said this meant it offered "exciting opportunities for pan-cancer, pan-population" immunotherapies not previously thought possible.
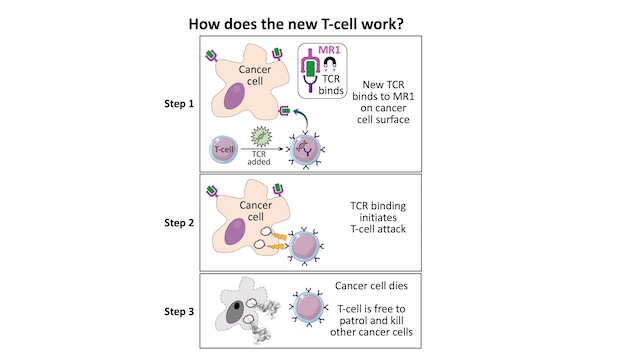
Photo by Cardiff University
How does this new TCR work?
Conventional T-cells scan the surface of other cells to find anomalies and eliminate cancerous cells—which express abnormal proteins—but ignore cells that contain only "normal" proteins.
The scanning system recognizes small parts of cellular proteins that are bound to cell-surface molecules called human leukocyte antigen (HLA), allowing killer T-cells to see what's occurring inside cells by scanning their surface.



