
Breaking News
 Zone 00: Permaculture for the Inner Landscape (No Land Required)
Zone 00: Permaculture for the Inner Landscape (No Land Required)
 Sam Bankman-Fried files for new trial over FTX fraud charges
Sam Bankman-Fried files for new trial over FTX fraud charges
 Big Tariff Refunds Are Coming. How Much and How Soon?
Big Tariff Refunds Are Coming. How Much and How Soon?
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Broad-spectrum solar breakthrough could efficiently produce hydrogen
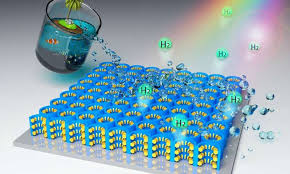
Hydrogen is viewed by many folks, particularly in Japan and Korea, as the clean-burning fuel that might power our vehicles in a low-emissions future. One way to produce hydrogen is to split it out of water. This is typically done by splitting water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity, but a potentially simpler and more efficient way to do it may be through photocatalytic water splitting, which uses light itself as the energy source instead of electricity, removing electricity production from the process altogether.
Nobody has yet managed to commercialize photocatalytic hydrogen production, but it's a hot area of research, and this OSU team claims it's discovered one of the most efficient photocatalytic molecules to date.
The molecule has shown a unique ability to use light from right across the visible spectrum. Where most previous photocatalysts have focused on high-energy ultraviolet wavelengths, this one can capture energy from ultraviolet, all the way through the visible spectrum and well into the near infrared range, meaning it can absorb up to 50 percent more solar energy than current solar cells.

 Iran & Epstein Fallout
Iran & Epstein Fallout


