
Breaking News
 ISIS Attacker Killed by ROTC Students + GDP Crashes to 0.7% + Senate Bans the Digital Dollar
ISIS Attacker Killed by ROTC Students + GDP Crashes to 0.7% + Senate Bans the Digital Dollar
 The Case for Gold: Why It Matters Now | Philip Patrick
The Case for Gold: Why It Matters Now | Philip Patrick
 "This will change HUMANITY!" Intel agencies using nanotech to control our thoughts
"This will change HUMANITY!" Intel agencies using nanotech to control our thoughts
 Doomed to Fail: Washington Lawmakers Don't Understand 3D Printing
Doomed to Fail: Washington Lawmakers Don't Understand 3D Printing
Top Tech News
 Musk Whips Out 'Macrohard' In Disruptive Tesla-xAI Bid To Shaft Software Companies
Musk Whips Out 'Macrohard' In Disruptive Tesla-xAI Bid To Shaft Software Companies
 This Bonkers Folding X-Plane Is One Step Closer to Hitting the Skies
This Bonkers Folding X-Plane Is One Step Closer to Hitting the Skies
 Smart 2-in-1 digital microscope goes desktop or handheld as needed
Smart 2-in-1 digital microscope goes desktop or handheld as needed
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
Powering Communication for an Interstellar Probe
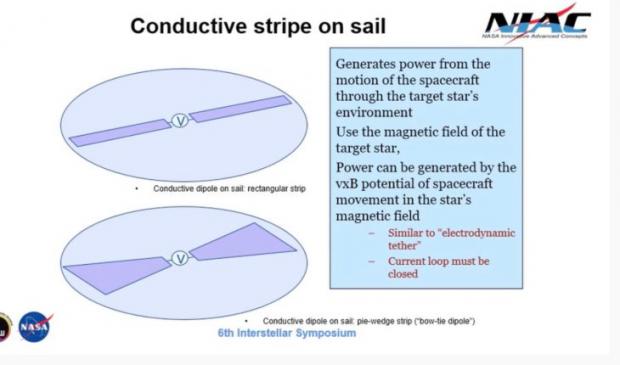
It was part of the 2019 Interstellar Symposium. The workshop focused on physics-based propulsion technologies that have the potential to meet the goal of launching an interstellar probe within the next century and achieving .1c transit velocity: Beamed Energy Propulsion, Fusion, and Antimatter.
The state-of-the-art of each was examined, and competing approaches to advancing the Technology Readiness Level (TRL) were presented and assessed for synthesis into a report that will serve as the blueprint for possible future interstellar propulsion technology development.
Geoffrey Landis looked at providing power for communication for an interstellar probe that weighs a couple of grams. He looks at using a system to generate power from a system that has been accelerated to 10-20% of the speed of light. The probe would interact with the interstellar plasma and with magnetic fields of the target solar system.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

