
Breaking News
 Iran War Hits Cyber, Food, Energy: Stryker Cyberattack, India Fertilizer Stoppage
Iran War Hits Cyber, Food, Energy: Stryker Cyberattack, India Fertilizer Stoppage
 Cork Stryker plants hit by suspected global Iranian-linked cyberattack
Cork Stryker plants hit by suspected global Iranian-linked cyberattack
270 WSM Ballistics From Major Manufacturers
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Newly-Developed Solar Cell Earns Two World Records for Its 'Extraordinary' Efficiency
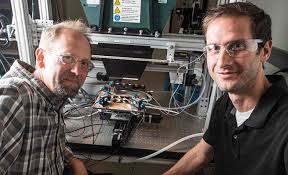
Scientists at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) have fabricated a solar cell with an efficiency of nearly 50%.
For perspective, the average solar cell has an efficiency rate of 15% to 20%, meaning it's capable of converting just a small fraction of absorbed sunlight into electricity.
The newly-developed six-junction solar cell, however, now holds the world record for the highest solar conversion efficiency at 47.1%, which was measured under concentrated illumination. A variation of the same cell also set the efficiency record under one-sun illumination at 39.2%.
"This device really demonstrates the extraordinary potential of multijunction solar cells," said John Geisz, a principal scientist in the High-Efficiency Crystalline Photovoltaics Group at NREL and lead author of a new paper on the record-setting cell.
The paper appeared in the journal Nature Energy this week.
To construct the device, NREL researchers relied on III-V materials—so called because of their position on the periodic table—that have a wide range of light absorption properties. Each of the cell's six junctions (the photoactive layers) is specially designed to capture light from a specific part of the solar spectrum.
The device contains about 140 total layers of various III-V materials to support the performance of these junctions, and yet is three times narrower than a human hair. Due to their highly efficient nature and the cost associated with making them, III-V solar cells are most often used to power satellites, which prize III-V's unmatched performance.
On Earth, however, the six-junction solar cell is well-suited for use in concentrator photovoltaics, said Ryan France, co-author and a scientist in the III-V Multijunctions Group at NREL.

 Now Its Time to PANIC
Now Its Time to PANIC
 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

