
Breaking News
 Democrats Announce State Of The Union Response Will Be Delivered By Bad Bunny
Democrats Announce State Of The Union Response Will Be Delivered By Bad Bunny
 American Attack on Iran: World War
American Attack on Iran: World War
 If You Think the US Wants To Bring Democracy to Iran, Watch What They're Currently Doing to Iraq
If You Think the US Wants To Bring Democracy to Iran, Watch What They're Currently Doing to Iraq
 The Scary Truth About Living in Big Cities During the Turbulent Times Ahead
The Scary Truth About Living in Big Cities During the Turbulent Times Ahead
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Simple Injection Could Be the Cure for Wrestlers and Athletes Suffering From 'Cauliflower Ear
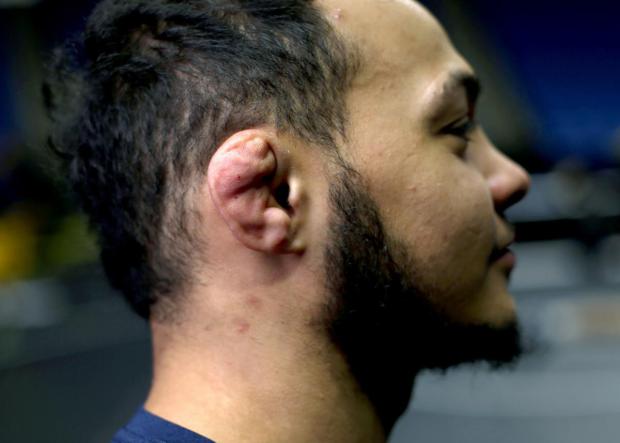
Chinese researchers have developed a new 3D-bioprinting machine capable of making new tissue without the need for traumatic surgery.
It means sports stars like Richie McCaw, Graham Rowntree, and Dan Cole won't have their retirement blighted with snide comments about their disfigured ears.
The international team used a non-invasive technique to 3D-bioprint new ears for mice, a procedure which creates layers of tissue similarly to how spare parts are built by conventional 3D printers in industry. Instead of ink, the researchers created a mix of cartilage cells and chemicals that were administered beneath the skin at the back of the ear. The new tissue began forming immediately, correcting genetically malformed "auricles" in the lab rodents—the visible part of the ear outside the head.
One month later, the cartilage had maintained its shape and been colonized by blood vessels and muscles to begin growing and renewing themselves normally.
The "bio-ink", which was described in the study published in Science Advances, is controlled using rays of near-infrared digital light, rather than UV light that is harmful to the cells.



