
Breaking News
 The Self-Sufficiency Myth No One Talks About
The Self-Sufficiency Myth No One Talks About
 We Investigated The Maui Fires and The Cover-Up is Worse Than We Thought | Redacted
We Investigated The Maui Fires and The Cover-Up is Worse Than We Thought | Redacted
 The Amish Secret to Keeping Pests Out of Your Garden Forever
The Amish Secret to Keeping Pests Out of Your Garden Forever
 Scott Ritter: Full-Scale War as Iran Attacks All U.S. Targets
Scott Ritter: Full-Scale War as Iran Attacks All U.S. Targets
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Spintronics Breakthrough Could Enable Vastly Higher Speed Data Technology
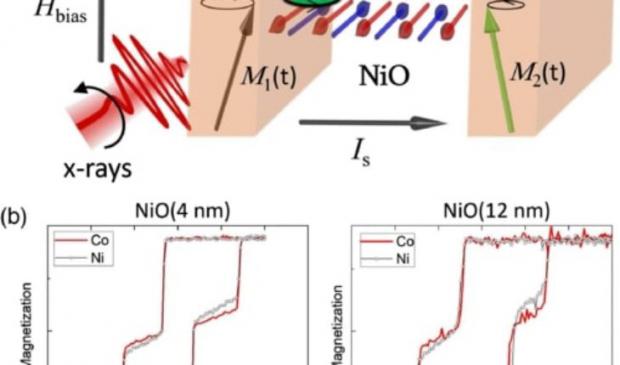
'Spin-based electronics or 'spintronics', that exploits spin current, has the potential to be not just significantly faster, but also more energy-efficient.
Scientists have recently discovered that some electrically insulating antiferromagnetic materials are exceptionally good conductors of pure spin current.
In the new research, scientists from Exeter, in collaboration with the Universities of Oxford, California Berkeley, and the Advanced and Diamond Light Sources, have experimentally demonstrated that high frequency alternating spin currents can be transmitted by, and sometimes amplified within, thin layers of antiferromagnetic NiO.
The results demonstrate that the spin current in thin NiO layers is mediated by evanescent spin waves, a mechanism akin to quantum mechanical tunneling.
The use of thin NiO layers for transfer and amplification of ac spin current at room temperature and gigahertz frequencies may lead to more efficient future wireless communication technology.
Insulating antiferromagnets have recently emerged as efficient and robust conductors of spin current. Element-specific and phase-resolved x-ray ferromagnetic resonance has been used to probe the injection and transmission of ac spin current through thin epitaxial NiO(001) layers. The spin current is found to be mediated by coherent evanescent spin waves of GHz frequency, rather than propagating magnons of THz frequency, paving the way towards coherent control of the phase and amplitude of spin currents within an antiferromagnetic insulator at room temperature.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

