
Breaking News
 China's Nightmarish New Bio Weapon Targets Race and Ethnicity
China's Nightmarish New Bio Weapon Targets Race and Ethnicity
 The Epstein Files Just EXPOSED the AI Mind Control Agenda (2026 Warning)
The Epstein Files Just EXPOSED the AI Mind Control Agenda (2026 Warning)
 Maxwell offers testimony if granted Trump clemency
Maxwell offers testimony if granted Trump clemency
 How RFK Jr's Guidelines Could Change Farming - Joel Salatin
How RFK Jr's Guidelines Could Change Farming - Joel Salatin
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Researchers Turn Red Bricks Into Supercapacitor Battery
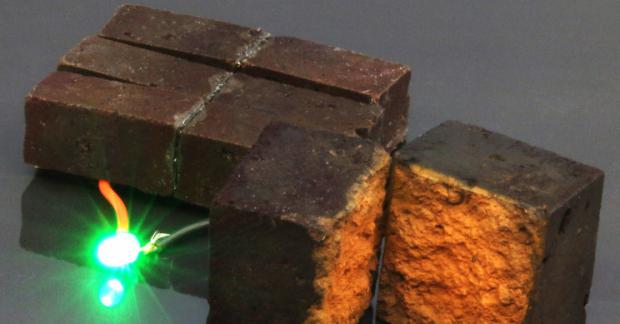
Red bricks, one of the world's most abundant and cheapest building materials, can be converted into batteries that can be charged to hold electricity, according to new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
If their "smart brick" concept is truly scalable, we might have whole new meanings for the concept of a self-sustainable home and a bricked battery.
The researchers behind the concept published their proof-of-concept on August 11 in Nature Communications, in which they showed a brick directly powering a green LED light (picture above).
"Our method works with regular brick or recycled bricks, and we can make our own bricks as well," Julio D'Arcy, assistant professor of chemistry explained in a press release.
This Ghostly 'Blue Whirl' Spinning Light Is Made of Three Distinct Flames
"As a matter of fact, the work that we have published in Nature Communications stems from bricks that we bought at Home Depot right here in Brentwood (Missouri); each brick was 65 cents," he continued.
Essentially, D'Arcy and colleagues, including Washington University graduate student Hongmin Wang, first author of the new study, detailed how to convert red bricks into a supercapacitor.
"In this work, we have developed a coating of the conducting polymer PEDOT, which is comprised of nanofibers that penetrate the inner porous network of a brick; a polymer coating remains trapped in a brick and serves as an ion sponge that stores and conducts electricity," D'Arcy said.
The iron oxide and rust in red bricks that give them their color are essential for triggering the polymerization reaction. The researchers say that walls made from these bricks have a potential for storing a large amount of energy.
"PEDOT-coated bricks are ideal building blocks that can provide power to emergency lighting," D'Arcy said. "We envision that this could be a reality when you connect our bricks with solar cells—this could take 50 bricks in close proximity to the load. These 50 bricks would enable powering emergency lighting for five hours.
"Advantageously, a brick wall serving as a supercapacitor can be recharged hundreds of thousands of times within an hour. If you connect a couple of bricks, microelectronics sensors would be easily powered."

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

