
Breaking News
 How Epstein Hijacked Bitcoin with Aaron Day
How Epstein Hijacked Bitcoin with Aaron Day
 The Federal Reserve is planned to inject $16 billion into the economy this week...
The Federal Reserve is planned to inject $16 billion into the economy this week...
 Dr. Rhonda Patrick: Fasting, Creatine, Brain Performance & Longevity Breakthroughs | PBD #740
Dr. Rhonda Patrick: Fasting, Creatine, Brain Performance & Longevity Breakthroughs | PBD #740
 HIGH ALERT! Americans Will Die for Israel's Evil War with Iran | Redacted w Clayton Morris
HIGH ALERT! Americans Will Die for Israel's Evil War with Iran | Redacted w Clayton Morris
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Record Time Measurement is Time for Light to Cross a Hydrogen Molecule
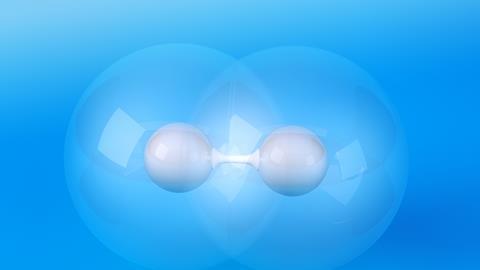
Using an electron interferometric technique researchers report a birth time delay on the order of a few hundred zeptoseconds (247 zeptoseconds) between two electron emissions from the two sides of molecular hydrogen, which is interpreted as the travel time of the photon across the molecule. The proposed technique is generally applicable to more complex systems, and further studies are necessary to support this interpretation.
A zeptosecond is a trillionth of a billionth of a second (10^-21 seconds).
A femtosecond equals 0.000000000000001 seconds, or 10^-15 seconds. Light travels 300 nanometers in a femtosecond.
An attosecond is 10^-18 seconds. Light travels 0.3 nanometers in an attosecond.
Light travels 0.07 nanometers or 70 picometers in 247 zeptoseconds.
This is the shortest timespan that has been successfully measured to date.
The scientists carried out the time measurement on a hydrogen molecule (H2) which they irradiated with X-rays from the synchrotron lightsource PETRA III at the Hamburg accelerator centre DESY. The researchers set the energy of the X-rays so that one photon was sufficient to eject both electrons out of the hydrogen molecule.
Electrons behave like particles and waves simultaneously, and therefore the ejection of the first electron resulted in electron waves launched first in the one, and then in the second hydrogen molecule atom in quick succession, with the waves merging.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

