
Breaking News
 Is the White House Actually the Overlook Hotel East?
Is the White House Actually the Overlook Hotel East?
 QatarEnergy Declares Force Majeure As One-Fifth Of Global LNG Supply Goes Dark
QatarEnergy Declares Force Majeure As One-Fifth Of Global LNG Supply Goes Dark
 Primary Losers: Crockett Cries 'Disenfranchisement', Crenshaw Crushed
Primary Losers: Crockett Cries 'Disenfranchisement', Crenshaw Crushed
 U.S. Submarine Sinks Iranian Warship In First Torpedo Kill Since WWII
U.S. Submarine Sinks Iranian Warship In First Torpedo Kill Since WWII
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Scientists capture world's first 3,200-megapixel photos
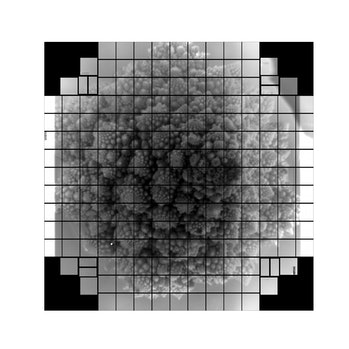
Scientists at the Menlo Park, California-based SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have taken the world's first 3,200-megapixel digital photos, using an advanced imaging device that's built to explore the universe.
"We will measure and catalog something like 20 billion galaxies." said Steven Kahn, director of the Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile. That observatory is where the world's largest digital camera will become the centerpiece of a monumental effort to map the night sky. The camera will spend 10 years capturing the most detailed images of the universe ever taken.
"Most parts of the night sky have actually never been imaged at all by telescopes." Kahn said. "No part of the sky has really been imaged with this kind of time, sequencing and time cadence, where you can watch how things change."
The team working on the camera just completed the focal plane, which is an array of imaging sensors more than two feet wide. (The equivalent focal length on an iPhone 11 camera is 26 millimeters.) It took the team about six months to assemble the sensors, largely because the sensors can easily crack if they touch each other during the installation process.
Since the camera isn't complete, scientists used a pinhole projector to test the focal plane. They snapped photos of an image of Vera C. Rubin (the late scientist the observatory is named for), the camera team, and a head of romanesco broccoli.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

