
Breaking News
 US Military Leaders Tell Troops Trump Is Waging Iran War To Bring Forth Second Coming Of Jesus
US Military Leaders Tell Troops Trump Is Waging Iran War To Bring Forth Second Coming Of Jesus
 Jim Rickards: "Cuba's Next" After Iran Strikes. Market Predictions on Oil, Gold and th
Jim Rickards: "Cuba's Next" After Iran Strikes. Market Predictions on Oil, Gold and th
 Gas prices soar as QatarEnergy halts LNG production after Iran attacks
Gas prices soar as QatarEnergy halts LNG production after Iran attacks
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Breakthrough Electronic Amoeba Analog Computer For Approximate Solving Traveling Salesman Problems
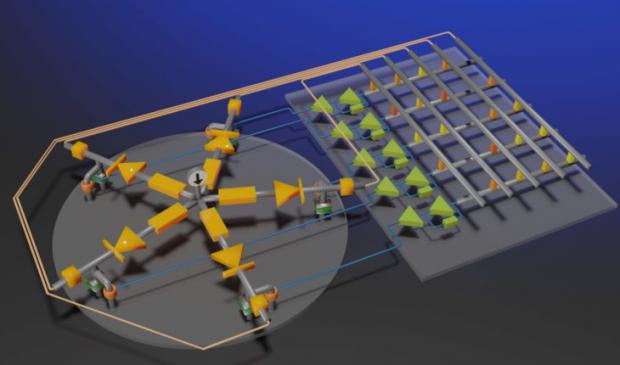
The salesman problem is this question: "Given a list of cities and the distances between each pair of cities, what is the shortest possible route that visits each city exactly once and returns to the origin city?". Having really good solutions for this class of problems means the US postal service, Fedex, UPS, airlines and the US military would save huge amounts of money. It is an NP-hard problem in combinatorial optimization, important in theoretical computer science and operations research.
Conventional digital computers, including supercomputers, are inadequate to solve these complex problems in practically permissible time as the number of candidate solutions they need to evaluate increases exponentially with the problem size. This is a combinatorial explosion. D-Wave Systems and others have created "Ising machines" and "quantum annealers," have been actively developed in recent years. There is complicated pre-processing to convert each task to the form they can handle and have a risk of presenting illegal solutions that do not meet some constraints and requests, resulting in major obstacles to the practical applications.
Approximation Algorithms
Various heuristics and approximation algorithms, which quickly yield good solutions, have been devised. These include the Multi-fragment algorithm. Modern methods can find solutions for extremely large problems (millions of cities) within a reasonable time which are with a high probability just 2–3% away from the optimal solution.
Exact algorithms
The most direct solution would be to try all permutations (ordered combinations) and see which one is cheapest (using brute-force search). The running time for this approach lies within a polynomial factor of {displaystyle O(n!)}O(n!), the factorial of the number of cities, so this solution becomes impractical even for only 20 cities.

 Bahrain's Big Breakout
Bahrain's Big Breakout RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

