
Breaking News
 BACKWARD ROLLING CONFIRMED: 1,624 Contracts Just Demanded Delivery NOW ($100 Silver is Inevitable)
BACKWARD ROLLING CONFIRMED: 1,624 Contracts Just Demanded Delivery NOW ($100 Silver is Inevitable)
SEMI-NEWS/SEMI-SATIRE: January 11, 2026 Edition
 "Appalling": Debanking Explodes To Record High In Britain
"Appalling": Debanking Explodes To Record High In Britain
 MTG explodes in astonishing f-bomb laden tirade as Trump orders Secret Service probe:
MTG explodes in astonishing f-bomb laden tirade as Trump orders Secret Service probe:
Top Tech News
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
 US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
 Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
 See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
Cryo-electron Microscopy Enables Breakthrough Imaging of Individual Atoms in Proteins
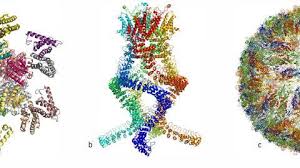
By achieving atomic resolution using cryogenic-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), researchers will be able to understand, in unprecedented detail, the workings of proteins that cannot easily be examined by other imaging techniques, such as X-ray crystallography.
Cryo-EM has been around for decades. It has long been able to determine the shape of flash-frozen samples by firing electrons at them and recording the resulting images. Advances in technology for detecting the ricocheting electrons and in image-analysis software catalyzed a 'resolution revolution' that started around 2013. This led to protein structures that were sharper than ever before — and nearly as good as those obtained from X-ray crystallography, an older technique that infers structures from diffraction patterns made by protein crystals when they are bombarded with X-rays.

 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this

