
Breaking News
 Microsoft Hands Over Encryption Keys #fyp #technews #microsoft #computer #secure
Microsoft Hands Over Encryption Keys #fyp #technews #microsoft #computer #secure
 Windows Now Requires Age Verification? #fyp #technews #windows #microsoft #privacy
Windows Now Requires Age Verification? #fyp #technews #windows #microsoft #privacy
 Iran's new supreme leader is named as Ali Khamenei's son Mojtaba - Iranian TV network report
Iran's new supreme leader is named as Ali Khamenei's son Mojtaba - Iranian TV network report
 Bill Pervs Out Over Epstein Memories, Hillary Goes Berserk, And They Both Lied: Top Viral Moments...
Bill Pervs Out Over Epstein Memories, Hillary Goes Berserk, And They Both Lied: Top Viral Moments...
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Oak Ridge Research Next Generation Cathode Free Lithium Ion Batteries
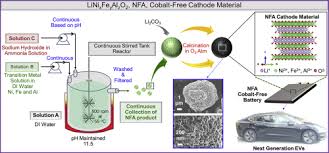
The new class called NFA, which stands for nickel-, iron- and aluminum-based cathode, is a derivative of lithium nickelate and can be used to make the positive electrode of a lithium-ion battery. These novel cathodes are designed to be fast charging, energy dense, cost effective, and longer-lasting.
With the rise in the production of portable electronics and electric vehicles throughout the world, lithium-ion batteries are in high demand. According to Ilias Belharouak, ORNL's scientist leading the NFA research and development, more than 100 million electric vehicles are anticipated to be on the road by 2030. Cobalt is a metal currently needed for the cathode which makes up the significant portion of a lithium-ion battery's cost.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

