
Breaking News
 Bret Weinstein's Thoughts on Charlie Kirk and Iran
Bret Weinstein's Thoughts on Charlie Kirk and Iran
 We Are the Villains in This Story
We Are the Villains in This Story
 My Prediction For the War with Iran
My Prediction For the War with Iran
 Foreign Hacker Cracked Into FBI's Epstein Files In 2023, Was 'Disgusted' At Child Sexual
Foreign Hacker Cracked Into FBI's Epstein Files In 2023, Was 'Disgusted' At Child Sexual
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Scientists Use Novel Ink With Calcium to 3D-Print 'Bone' With Living Cells
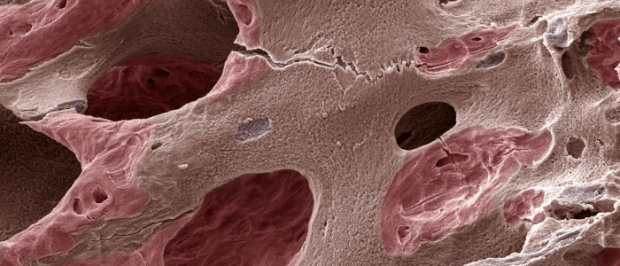
Scientists from UNSW Sydney have developed a ceramic-based ink that may allow surgeons in the future to 3D-print bone parts complete with living cells that could be used to repair damaged bone tissue.
Using a 3D-printer that deploys a special ink made up of calcium phosphate, the scientists developed a new technique, known as ceramic omnidirectional bioprinting in cell-suspensions (COBICS), enabling them to print bone-like structures that harden in a matter of minutes when placed in water.
While the idea of 3D-printing bone-mimicking structures is not new, this is the first time such material can be created at room temperature – complete with living cells – and without harsh chemicals or radiation, says Dr Iman Roohani from UNSW's School of Chemistry.
"This is a unique technology that can produce structures that closely mimic bone tissue," he said, pointing to repairs of bone defects caused by accidents or cancer.
Associate Professor Kristopher Kilian who co-developed the breakthrough technology with Dr Roohani says the fact that living cells can be part of the 3D-printed structure, together with its portability, make it a big advance on current state-of-the-art technology.
Up until now, he says, making a piece of bone-like material to repair bone tissue of a patient involves first going into a laboratory to fabricate the structures using high-temperature furnaces and toxic chemicals.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

