
Breaking News
SEMI-NEWS/SEMI-SATIRE: February 22, 2026 Edition
 The Domino Effect: How a U.S. Attack on Iran Could Unleash Global Catastrophe
The Domino Effect: How a U.S. Attack on Iran Could Unleash Global Catastrophe
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Tripling Optical Storage With New Encoding Approach
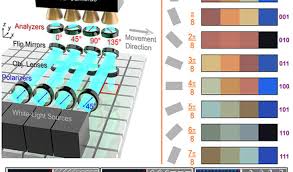
This will allow more data to be stored and for that data to be read at a quicker rate. Rather than using the traditional dots and dashes as commonly used in these technologies, the Purdue innovators encode information in the angular position of tiny antennas, allowing them to store more data per unit area.
This technology can also be used for security tagging and cryptography.
Above – The proposed anisotropic metasurface from Purdue University innovators has significant potential for high-density optical data storage, dynamic color image display, and encryption.
"The storage capacity greatly increases because it is only defined by the resolution of the sensor by which you can determine the angular positions of antennas," said Alexander Kildishev, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering in Purdue's College of Engineering. "We map the antenna angles into colors, and the colors are decoded."

 TGIF: Immigration and Culture
TGIF: Immigration and Culture Does It Smell Like Victory?
Does It Smell Like Victory?


