
Breaking News
Part 4: Immigration Is Killing America: Here Are The Results Coming
 2026-03-05 Ernest Hancock interviews Dr Phranq Tamburri (Trump Report) MP3 (MP4 to be loaded shortly
2026-03-05 Ernest Hancock interviews Dr Phranq Tamburri (Trump Report) MP3 (MP4 to be loaded shortly
 S3E8: Your Money, Your Data, Your Blood, All Stolen
S3E8: Your Money, Your Data, Your Blood, All Stolen
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Cartilage-inspired material may find use in self-lubricating bearings
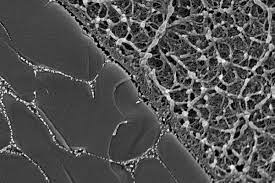
Cartilage covers the ends of the bones in joints such as our knees, letting them move smoothly against one another without wearing down the bone tissue underneath. It's made up of a porous matrix of collagen fibers, proteoglycan proteins, and elastin protein fibers. That matrix absorbs a viscous liquid known as synovial fluid, which is produced in the joints.
As the joint moves, the interfacing cartilage surfaces gradually release that fluid, providing lubrication. At the same time, the absorbed fluid also helps the cartilage to withstand being irreversibly deformed by compressive forces, thanks to a hydroelastic effect. And while researchers have previously tried to create artificial cartilage, they've typically used soft hydrogels that can't cope with such forces.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

