
Breaking News
 The Domino Effect: How a U.S. Attack on Iran Could Unleash Global Catastrophe
The Domino Effect: How a U.S. Attack on Iran Could Unleash Global Catastrophe
 The True History of Glyphosate, Derived from Deadly Organophosphate Nerve Agents like Sarin...
The True History of Glyphosate, Derived from Deadly Organophosphate Nerve Agents like Sarin...
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Smart bandage would use light to indicate infections
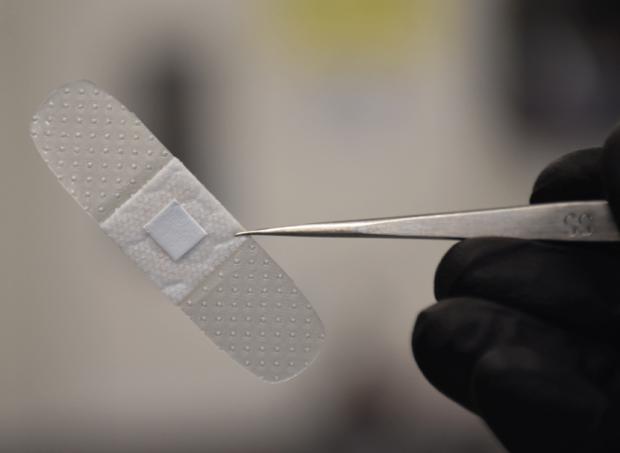

Developed by scientists at the University of Rhode Island, the experimental bandage contains modified single-walled carbon nanotubes, which are securely embedded within the dressing's individual polymer fibers. This arrangement keeps the nanotubes from leaching into the wound, yet still allows them to react to chemical compounds within the wound site.
One such compound, hydrogen peroxide, is produced by the body's white blood cells when pathogenic bacteria are present. That chemical in turn affects the color and intensity at which the nanotubes fluoresce when exposed to bright light. A compact device placed over the bandage could both trigger and analyze that fluorescence, subsequently transmitting an alert to a separate gadget such as a smartphone, if necessary.
"The hope is that the device will diagnose an infection at an early stage, necessitating fewer antibiotics and preventing drastic measures, such as limb amputation," says Asst. Prof. Daniel Roxbury, who worked on the project with former grad student Mohammad Moein Safaee. "We envision this being particularly useful in those with diabetes, where the management of chronic wounds is routine."
Plans now call for the bandage to be tested on live cultured cells in petri dishes, potentially followed by testing on lab mice.

 TGIF: Immigration and Culture
TGIF: Immigration and Culture Does It Smell Like Victory?
Does It Smell Like Victory?


