
Breaking News
 Free Ian Freeman: Defend Financial Privacy and Justice - Sign the petition
Free Ian Freeman: Defend Financial Privacy and Justice - Sign the petition
 Charlie Robinson with Tim James, Marjory Wildcraft & Patrick Henningsen:
Charlie Robinson with Tim James, Marjory Wildcraft & Patrick Henningsen:
 It's Time To Reopen The Franklin Child Prostitution Case After Epstein Revelations
It's Time To Reopen The Franklin Child Prostitution Case After Epstein Revelations
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Nanoparticle urine test diagnoses cancer and pinpoints its location
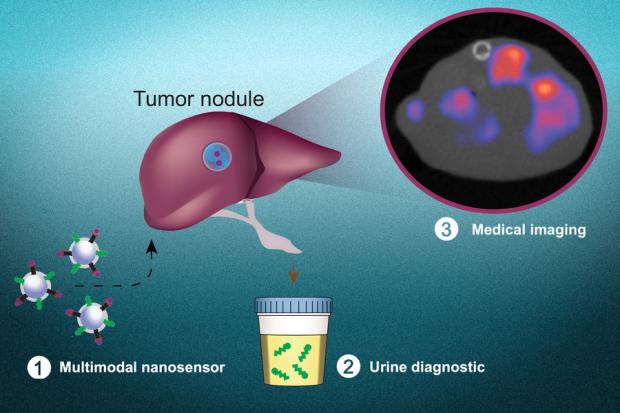
The MIT system is built around a specially designed nanoparticle that can produce "synthetic biomarkers" in urine if a person has cancer, and in previous tests it has proved promising at this job. But the problem is, it couldn't tell where in the body the tumors were located. Now, the team has added this function.The method by which the nanoparticles detect cancer is quite clever. To escape their point of origin and spread throughout the body, many cancers use enzymes called proteases which slice through proteins in the extracellular matrix. The diagnostic nanoparticles are coated in peptides that can also be cut up by these proteases, so if there are tumors present somewhere, the nanoparticles will bear the scars of their encounters by the time they reach the urine.

 The Question Not Being Asked
The Question Not Being Asked

