
Breaking News
 Swiss vote places right to use cash in country's constitution
Swiss vote places right to use cash in country's constitution
 ALPHABET ISSUES 100Y BOND (A MOTOROLA MOMENT?)
ALPHABET ISSUES 100Y BOND (A MOTOROLA MOMENT?)
 THIS E6B MERCURY AIRPLANE IS THE NUCLEAR COMMAND AND CONTROL CENTER TO DIRECT NUCLEAR ATTACK.
THIS E6B MERCURY AIRPLANE IS THE NUCLEAR COMMAND AND CONTROL CENTER TO DIRECT NUCLEAR ATTACK.
 Hidden Object Superpower for Robots!
Hidden Object Superpower for Robots!
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Researchers discover revolutionary material that could shatter limits of traditional solar panels
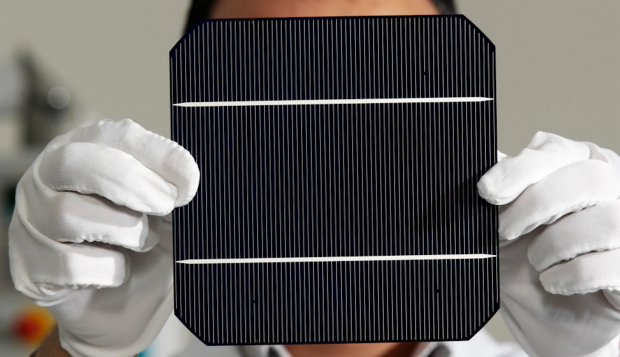
Researchers in Japan have discovered a breakthrough that could make solar panels more efficient than ever, according to SciTechDaily. This means cheaper energy bills and cleaner air for everyone.
Traditional solar panels have always hit a ceiling in terms of how much sunlight they can turn into electricity. It's like trying to fill a cup that can only hold so much water. There's been a limit to how much energy we could capture — until now.
Enter a revolutionary material with a fancy name: alpha-phase indium selenide. Unlike regular solar cells that waste some of the sun's energy, this material can capture and use more of the sunlight that hits it. Think of it like upgrading from a regular drinking straw to an extra-wide smoothie straw. You're able to take in more at once.



