
Breaking News
 The Epstein Files: A Peek Behind the Dark Curtain, Pt. 1
The Epstein Files: A Peek Behind the Dark Curtain, Pt. 1
 Make Your Own Herbal Tea Blends and Save $$$
Make Your Own Herbal Tea Blends and Save $$$
 Prince Andrews Arrested, Trump Releasing Alien Files, Supreme Court Tariff Decision...
Prince Andrews Arrested, Trump Releasing Alien Files, Supreme Court Tariff Decision...
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
The 'holy grail' of batteries:
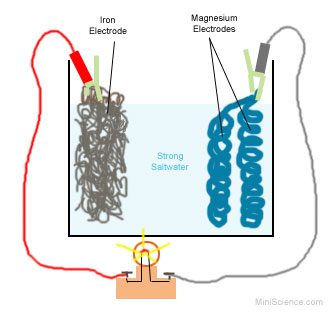
An 'iron-air' battery has been developed in the US that can store electricity from wind or solar power stations for days at a time, slowly discharging it to the grid.
It will help tackle climate change by reducing the need for fossil fuel power plants, according to technology startup Form Energy, from Massachusetts, US.
The Iron-Air battery is a 'new class of cost-effective, multi-day energy storage system,' that can feed electricity for 100 hours at 1/10th the cost of lithium-Ion, the 'holy grail' in terms of renewable energy technology.
It is made using iron, one of the most common elements on Earth, and works by breathing in oxygen, converting iron to rust, and turning rust back to iron.
As it takes in the oxygen and converts the iron back and forth it is charging and discharging the battery, a process that keeps the energy stored for a longer period.
The batteries are too heavy for use in electric cars, according to the firm, who say they are designed to meet the challenge of keeping a constant power supply.
If development continues at pace, Form Energy hope the first batteries will be working to supply the grid by 2025.
This will solve one of the most elusive problems facing renewable energy, that is how to cheaply store large amounts of electricity and supply it to power grids when the sun isn't shining for solar panels or wind isn't blowing for turbines.
Solar and wind resources are the lowest marginal cost sources of electricity in most of the world, but they don't provide a constant supply like fossil fuel power plants.

 Free Grocery Stores in NYC?
Free Grocery Stores in NYC? 

