
Breaking News
Part 4: Immigration Is Killing America: Here Are The Results Coming
 2026-03-05 Ernest Hancock interviews Dr Phranq Tamburri (Trump Report) MP3 (MP4 to be loaded shortly
2026-03-05 Ernest Hancock interviews Dr Phranq Tamburri (Trump Report) MP3 (MP4 to be loaded shortly
 S3E8: Your Money, Your Data, Your Blood, All Stolen
S3E8: Your Money, Your Data, Your Blood, All Stolen
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Bionic arm allows amputees to feel with fake fingers: Prosthetic combines intuitive motor control...
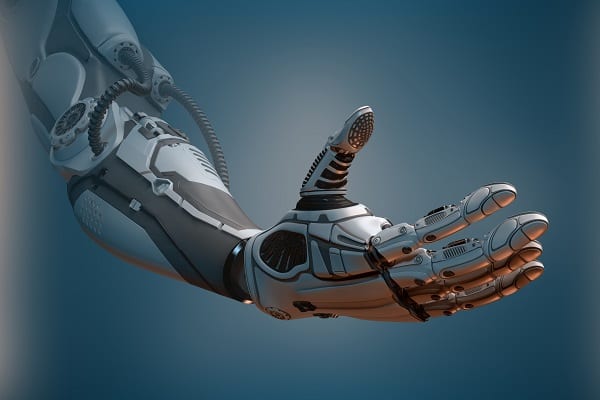
A bionic arm that combined intuitive motor control, touch and grip will allow amputees feel the sensation of feeling objects, its developers claim.
This is the first prosthetic limb that is able to test all key functions of a hand at the same time, and uses a brain-computer interface to trigger the interaction.
Lead investigator Professor Paul Marasco, of the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, said test subjects felt one of their hands was moving, even though they didn't have a hand, and felt as if their fingers were touching things, even though they had no fingers.
Putting touch, grip and motor control together, worked to trick the senses and brain of the wearer into thinking the prosthetic was a real human hand, Prof Marasco said.
It links to limb nerves which send impulses from the patient's brains to the prosthetic when they want to use or move it, and the arm receives physical information from the environment through sensors, sending it back into the brain through nerves.
The US team started out with a standard-of-care, off the shelf prosthetic arm which was then fitted with their new complex bionic system.
Tests on volunteers found that wearers could move their prosthetic arm more intuitively and feel sensations of touch and movement at the same time.
The two way communication, between brain and arm sensors, allowed the volunteers to perform a range of tasks similar to a non-amputee, they found.
'These findings are an important step towards providing people with amputation with complete restoration of natural arm function,' said Prof Marasco.



