
Breaking News
Part 4: Immigration Is Killing America: Here Are The Results Coming
 2026-03-05 Ernest Hancock interviews Dr Phranq Tamburri (Trump Report) MP3 (MP4 to be loaded shortly
2026-03-05 Ernest Hancock interviews Dr Phranq Tamburri (Trump Report) MP3 (MP4 to be loaded shortly
 S3E8: Your Money, Your Data, Your Blood, All Stolen
S3E8: Your Money, Your Data, Your Blood, All Stolen
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
In a First, Surgeons Attached a Pig Kidney to a Human -- and It Worked
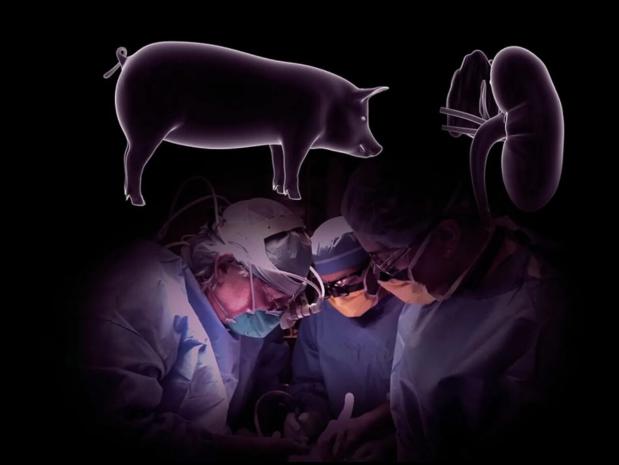
Although many questions remain to be answered about the long-term consequences of the transplant, which involved a brain-dead patient followed only for 54 hours, experts in the field said the procedure represented a milestone.
"We need to know more about the longevity of the organ," said Dr. Dorry Segev, professor of transplant surgery at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine who was not involved in the research. Nevertheless, he said: "This is a huge breakthrough. It's a big, big deal."
Researchers have long sought to grow organs in pigs suitable for transplantation into humans. A steady stream of organs — which could eventually include hearts, lungs and livers — would offer a lifeline to the more than 100,000 Americans currently on transplant waiting lists, including the 90,240 who need a kidney. Twelve people on the waiting lists die each day.
An even larger number of Americans with kidney failure — more than a half million — depend on grueling dialysis treatments to survive. In large part because of the scarcity of human organs, the vast majority of dialysis patients do not qualify for transplants, which are reserved for those most likely to thrive after the procedure.
The surgery, carried out at N.Y.U. Langone Health, was first reported by USA Today on Tuesday. The research has not yet been peer-reviewed nor published in a medical journal.
The transplanted kidney was obtained from a pig genetically engineered to grow an organ unlikely to be rejected by the human body. In a close approximation of an actual transplant procedure, the kidney was attached to a person who had suffered brain death and was maintained on a ventilator.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

