
Breaking News
 America's Streets Are Filled With Poop, And Billions Of Gallons Of Untreated Wastewater...
America's Streets Are Filled With Poop, And Billions Of Gallons Of Untreated Wastewater...
 3 Million Pages of Child Sex Trafficking, So, What Is the FBI Doing?
3 Million Pages of Child Sex Trafficking, So, What Is the FBI Doing?
 Communists Once Again Suck At Hockey
Communists Once Again Suck At Hockey
 Grand Theft World Podcast 274 | Epstein Apocalypse with Guest Santos Bonacci
Grand Theft World Podcast 274 | Epstein Apocalypse with Guest Santos Bonacci
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Researchers discover direct gut-brain communication pathway
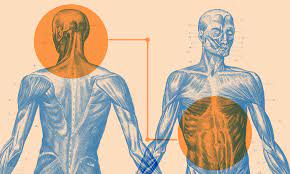
One of the most compelling emerging areas in medical science is the relationship between the gut and the brain. Recent research has uncovered fascinating ways these two distinct parts of the body communicate with each other, from the discovery of novel gut cells that can nearly instantly engage neural synapses, to the revelation that certain types of bacteria in the gut can influence the activity of immune cells in the brain.Most of these gut-brain discoveries involve bacteria indirectly influencing the brain, such as through releasing molecules that trigger cascades of other mechanisms. But this new study describes a novel way that bacteria can directly modulate the activity of certain clusters of neurons.



