
Breaking News
 America's Streets Are Filled With Poop, And Billions Of Gallons Of Untreated Wastewater...
America's Streets Are Filled With Poop, And Billions Of Gallons Of Untreated Wastewater...
 3 Million Pages of Child Sex Trafficking, So, What Is the FBI Doing?
3 Million Pages of Child Sex Trafficking, So, What Is the FBI Doing?
 Communists Once Again Suck At Hockey
Communists Once Again Suck At Hockey
 Grand Theft World Podcast 274 | Epstein Apocalypse with Guest Santos Bonacci
Grand Theft World Podcast 274 | Epstein Apocalypse with Guest Santos Bonacci
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Discovered: The genetic flaw that triggers skin cancer
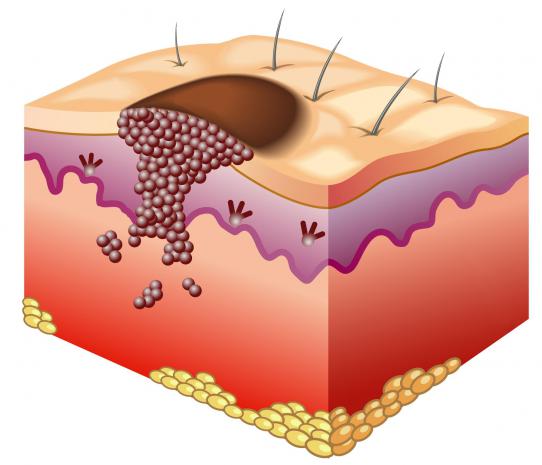
Up to 70 per cent of cases of malignant melanoma could be sparked by a genetic mutation caused by ageing and over-exposure to the sun.
Scientists at The Institute of Cancer Research had previously linked the rogue version of the so-called BRAF gene to the disease but did not know if it actually caused the cancer.
Now, the same group of researchers has shown that acquiring the BRAF mutation can be the first event in the cascade of genetic changes that eventually leads to melanoma, the most deadly form of skin cancer.
While the mutation could occur naturally, the odds of it appearing are likely to be exacerbated by intensive exposure to the sun.
Lead author Professor Richard Marais from the institute said: 'We know that excessive sun exposure is the main cause of skin cancer, but not much is known about the genetics behind it.
'Our study shows that the genetic damage of BRAF is the first step in skin cancer development.
'Understanding this process will help us develop more effective treatments for the disease.'
There are around 9,500 new cases of malignant melanoma and more than 2,300 deaths from the disease each year in the UK.
Over-exposure to sunlight causes at least two thirds of all malignant melanomas and up to 90 per cent of other skin cancers. This excessive exposure damages DNA and causes genetic mutations.



