
Breaking News
SEMI-NEWS/SEMI-SATIRE: March 1, 2026 Edition
 Clinton's Epstein Depositions + Paramount WINS WarnerBros Deal | PBD #748
Clinton's Epstein Depositions + Paramount WINS WarnerBros Deal | PBD #748
 Space is the AI Endgame for AI Scaling
Space is the AI Endgame for AI Scaling
 AI Winner Will Scale AI Energy and Compute on Earth and in Space Why XAI, SpaceX and Tesla Win
AI Winner Will Scale AI Energy and Compute on Earth and in Space Why XAI, SpaceX and Tesla Win
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Scientists Stumble on New Way to 'Hack' Photosynthesis For Renewable Energy
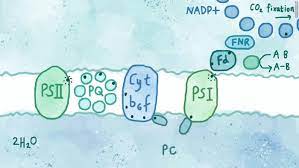
While trying to figure out if it were possible to extract electrons from a known process in the early stages of photosynthesis, the scientists instead found an entirely-new electron transfer pathway, which for those who remember their biology 101, is the metabolic method that extracts the most energy from food.
The study's authors believe this new understanding of photosynthesis could create new and more efficient ways of harnessing the process's power to generate biofuels.
The research team, comprised of scientists from across the globe, first set out to understand why a ring-shaped molecule called a 'quinone' is able to steal electrons from the photosynthetic process
Quinones, which are common in nature, are able to easily accept and give away electrons.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

