
Breaking News
 The Economic Impact Of This Horrifying War With Iran Is Not Going To Be Pretty
The Economic Impact Of This Horrifying War With Iran Is Not Going To Be Pretty
 A Conversation With Tommy Robinson -- SF689
A Conversation With Tommy Robinson -- SF689
 Hungary Detains Ukrainians Transporting Tens Of Millions In Cash & Gold
Hungary Detains Ukrainians Transporting Tens Of Millions In Cash & Gold
 Dem Lawmakers Demand Probe Into Pentagon Officials Saying Iran War 'God's Divine Plan'
Dem Lawmakers Demand Probe Into Pentagon Officials Saying Iran War 'God's Divine Plan'
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Exercise's Secret for Preventing Alzheimer's Disease Discovered by Scientists
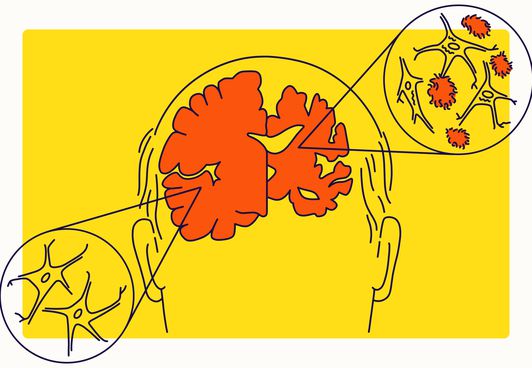
A new study has discovered why exercise may prevent Alzheimer's disease, potentially paving the way for new treatments for the currently incurable condition.
Experts at Massachusetts General Hospital found that during exercise, the body releases a hormone called irisin. This hormone has been shown to reduce the brain plaques and tangles commonly associated with Alzheimer's disease onset.
While physical exercise has consistently demonstrated its ability to reduce amyloid beta deposits in mouse experiments, the exact mechanisms remained unclear until now. The study, published in the journal Neuron, clears up this mystery and also suggests potential avenues for prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's — the most common form of dementia.
The Mass General team pioneered the development of the first 3D human cell culture models for Alzheimer's. These models showcase two primary characteristics of the disease: the formation of amyloid beta deposits and subsequent tau tangles in the brain.
It's well-documented that exercise elevates the levels of the muscle-derived hormone irisin, which not only helps regulate glucose and lipid metabolism in fat tissues but also enhances energy expenditure by promoting the conversion of white fat into brown fat. Earlier research indicated that irisin is present in both human and mouse brains. However, its levels are diminished in individuals with Alzheimer's. With this knowledge, the research team introduced irisin to their 3D cell culture model of Alzheimer's.



