
Breaking News
Part 4: Immigration Is Killing America: Here Are The Results Coming
 2026-03-05 Ernest Hancock interviews Dr Phranq Tamburri (Trump Report) MP3 (MP4 to be loaded shortly
2026-03-05 Ernest Hancock interviews Dr Phranq Tamburri (Trump Report) MP3 (MP4 to be loaded shortly
 S3E8: Your Money, Your Data, Your Blood, All Stolen
S3E8: Your Money, Your Data, Your Blood, All Stolen
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Your WiFi Can See You
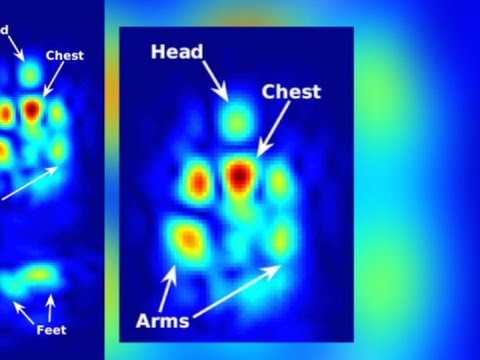
They found hot pockets in the house, which were used to obtain a search warrant and subsequently bust Kyllo.
Fortunately, a 5-4 Supreme Court decision ruled the scan an unlawful search under the Fourth Amendment, requiring a warrant the police did not obtain. Score one for privacy, but the government is about to have a far more controversial and dangerous tool at its disposal to monitor what's going on inside your home.
Unlike a thermal imager, this device is already in your home – and you put it there.
How It Works
WiFi is electromagnetic waves in the 2.4 and 5 GHz ranges. It's the same thing as the light you see, only it can penetrate walls due to its much longer wavelength. Just like light (and echolocation) these waves also reflect off various surfaces and, when reconstructed properly, can be used to create an image.
Development of this technology goes back at least as far as July 2005, where researchers claimed at an IEEE Symposium that they had created an ultra-wideband high-resolution short pulse imaging radar system operating around 10 GHz. The applications for which were explicitly for military and police use, providing them with "enhanced situation awareness."
A few years later, in 2008, researchers at UC Santa Barbara created an initial approach for imaging with WiFi that they presented at IEEE ACC 2009. A year later they demonstrated the feasibility of this approach.



