
Breaking News
 Will Trump's Legacy Be Saved If He Starts World War III?
Will Trump's Legacy Be Saved If He Starts World War III?
 AI-powered warfare: Anthropic's Claude model used in Venezuelan military raid
AI-powered warfare: Anthropic's Claude model used in Venezuelan military raid
 U.S. deploys second aircraft carrier to Middle East amid escalating tensions with Iran
U.S. deploys second aircraft carrier to Middle East amid escalating tensions with Iran
 The Last Line of Defense: Why America's sheriffs are the last barrier against tyranny
The Last Line of Defense: Why America's sheriffs are the last barrier against tyranny
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Light therapy helps the brain clear out toxic Alzheimer's proteins
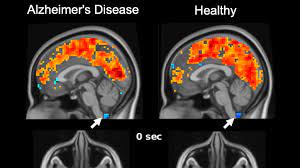
Despite their tireless efforts, researchers have been unable to develop a safe and effective way of treating Alzheimer's disease (AD) using pharmaceuticals, which has meant turning to non-pharmaceutical methods. A new study has demonstrated the therapeutic potential of light therapy, or phototherapy, in treating AD, showing promising results in mice that the researchers hope can be just as effective in humans. In the study, the researchers used photobiomodulation (PBM), a non-pharmaceutical therapy that employs red and near-infrared lights to stimulate the body to heal itself. There's evidence to suggest that PBM causes an increase in metabolism and microcirculation in the brain, in addition to reversing oxidative stress and inflammation. Recent studies discovered that PBM can stimulate the brain's lymphatic system to remove wastes and toxins.



