
Breaking News
 Zone 00: Permaculture for the Inner Landscape (No Land Required)
Zone 00: Permaculture for the Inner Landscape (No Land Required)
 Sam Bankman-Fried files for new trial over FTX fraud charges
Sam Bankman-Fried files for new trial over FTX fraud charges
 Big Tariff Refunds Are Coming. How Much and How Soon?
Big Tariff Refunds Are Coming. How Much and How Soon?
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Robotic Hand with Bones, Ligaments and Tendons Created for First Time Using 3D Printing
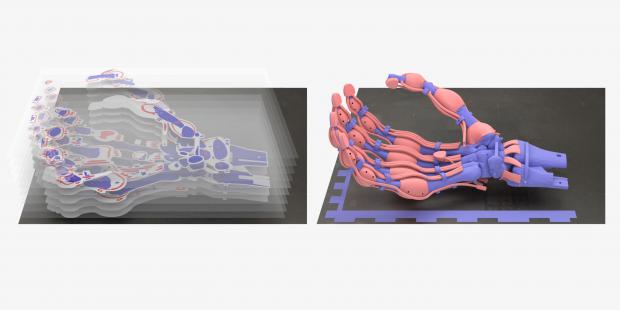
The various polymers can be fine-tuned to replicate the elasticity or rigidity of a human hand, representing a major advancement over existing 3D-printed prosthetics.
While 3D printing technology was previously limited to fast-curing plastics, researchers have now made it suitable for slow-curing plastics as well.
They say these materials have "decisive" advantages as they have enhanced elastic properties and are more durable and robust.
The use of such polymers is made possible by new technology developed by researchers at ETH Zurich in Switzerland and a US startup from Mass. Institute of Technology which can be used to create delicate structures and parts with cavities as desired. InkBit from MIT now offers the technology and prints complex objects on customer request.The technology also makes it easy to combine soft, elastic, and rigid materials.
"We wouldn't have been able to make this hand with the fast-curing polyacrylates we've been using in 3D printing so far," said Thomas Buchner, a doctoral student from ETH Zurich who led the authorship of the paper published on their work.
"We're now using slow-curing thiolene polymers. These have very good elastic properties and return to their original state much faster after bending than polyacrylates," he said, adding this makes them ideal for making complex prosthetics.

 Iran & Epstein Fallout
Iran & Epstein Fallout


