
Breaking News
 The Economic Impact Of This Horrifying War With Iran Is Not Going To Be Pretty
The Economic Impact Of This Horrifying War With Iran Is Not Going To Be Pretty
 A Conversation With Tommy Robinson -- SF689
A Conversation With Tommy Robinson -- SF689
 Hungary Detains Ukrainians Transporting Tens Of Millions In Cash & Gold
Hungary Detains Ukrainians Transporting Tens Of Millions In Cash & Gold
 Dem Lawmakers Demand Probe Into Pentagon Officials Saying Iran War 'God's Divine Plan'
Dem Lawmakers Demand Probe Into Pentagon Officials Saying Iran War 'God's Divine Plan'
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Nanoscale spinal implant helps restore mobility in paralyzed limbs
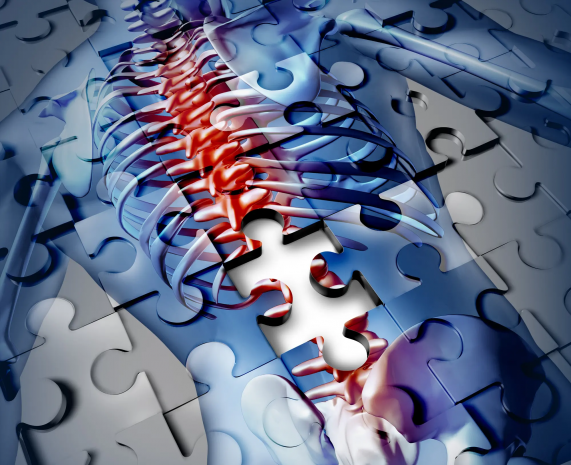
Spinal injuries interrupt the flow of electrical signals from the brain to the lower parts of the body, reducing mobility and in severe cases leading to total paralysis. Spinal stimulators are devices that can be surgically implanted into a patient's spine to bypass the injury site and restore some mobility. Unfortunately, these are often bulky, require surgery, and have precision issues.
For the new study, the Johns Hopkins team developed a much smaller device that's flexible and stretchable. It's placed into a different site than other stimulators – the ventrolateral epidural surface, which is not only close to motor neurons for better precision, but it can just be injected into place with a regular syringe, no surgery required. Tests in paralyzed mice proved promising.



