
Breaking News
 The Self-Sufficiency Myth No One Talks About
The Self-Sufficiency Myth No One Talks About
 We Investigated The Maui Fires and The Cover-Up is Worse Than We Thought | Redacted
We Investigated The Maui Fires and The Cover-Up is Worse Than We Thought | Redacted
 The Amish Secret to Keeping Pests Out of Your Garden Forever
The Amish Secret to Keeping Pests Out of Your Garden Forever
 Scott Ritter: Full-Scale War as Iran Attacks All U.S. Targets
Scott Ritter: Full-Scale War as Iran Attacks All U.S. Targets
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Where does our 'brain waste' go? Scientists think they've figured it out and can use it.
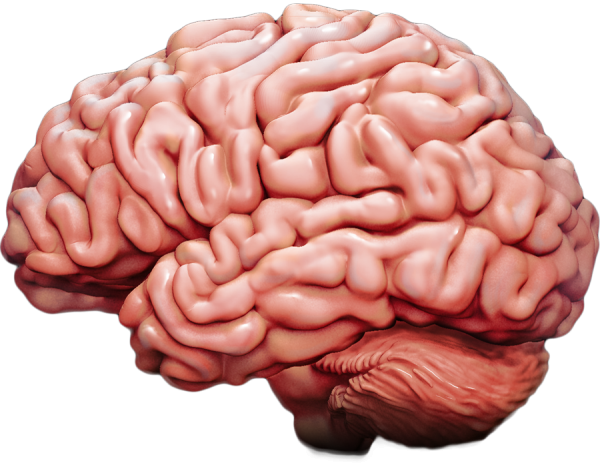
Scientists are beginning to understand how the brain flushes out waste products in order to stay healthy and fend off neurological diseases.
Two teams of scientists from Washington have uncovered signs that a slow wave of electricity that pulses through the brain during sleep pushes waste products, including the protein closely associated with Alzheimer's disease, from deep in the brain to its surface.
A vein passing through the brain then acts as a pipe to carry waste products out through the barrier that separates the brain and the rest of the body. This deposits them into the bloodstream to be filtered out by the kidneys.
But if the disposal system stops working correctly, which can occur with aging, in cases of traumatic brain injury, and chronic stress, those waste products can accumulate in the brain.
It may also allow immune cells to penetrate the organ, leading to inflammation linked to degenerative brain disorders.
The study was conducted in mice, but researchers believe their findings match up with research on potential causes of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias.
In February, scientists led by Dr Jonathan Kipnis, a neurologist at Washington University in St Louis, answered the question of how the brain gets waste out through the rigid protective barrier without using the body's lymphatic system, a network that drains fluids throughout the body.
The brain is not part of that system and its waste disposal pathway is known as the glymphatic system. It clears out waste generated by energy-consuming metabolic processes - all the chemical processes continuously working in the body to ensure it functions correctly - such as carbon dioxide, damaged proteins and dead cells.
Scientists uncovered exit points around the brain from which cerebrospinal fluid, which carries waste, flowed out to the thick membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord and into the bloodstream, where the body's lymphatic vessels took over to clear it out.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

