
Breaking News
 Swiss vote places right to use cash in country's constitution
Swiss vote places right to use cash in country's constitution
 ALPHABET ISSUES 100Y BOND (A MOTOROLA MOMENT?)
ALPHABET ISSUES 100Y BOND (A MOTOROLA MOMENT?)
 THIS E6B MERCURY AIRPLANE IS THE NUCLEAR COMMAND AND CONTROL CENTER TO DIRECT NUCLEAR ATTACK.
THIS E6B MERCURY AIRPLANE IS THE NUCLEAR COMMAND AND CONTROL CENTER TO DIRECT NUCLEAR ATTACK.
 Hidden Object Superpower for Robots!
Hidden Object Superpower for Robots!
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Buoyancy-driven hybrid energy platform moves to full-scale pilot
Next step: a full-scale pilot.
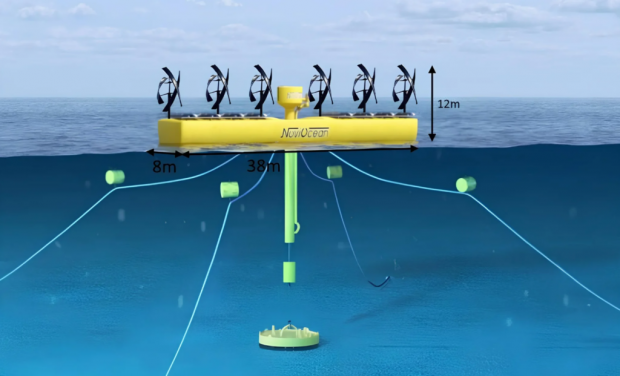
This renewable energy platform will have a relatively small footprint once built at full size: 38 x 9 m (125 x 30 ft), the platform itself extending some 4 m (13 ft) above the water surface, and a further 12 m (39 ft) down below. Tiny, then, in comparison to some of the monstrous offshore wind turbines we're starting to see, like the colossal 20-MW MingYang turbine that's currently the world's largest.
But it's designed to punch above its 140-ton weight, and deliver energy more consistently than any single-method generator.
How does it work?
When the Sun's shining, it powers some 700 square meters (7,535 sq ft), or 50 kW worth of solar panels. When the wind's blowing – and most of the world's best wind resources are offshore where this thing will live – it'll drive a series of six helical-bladed, vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWT). And it'll also harvest up to 650 kW of energy from the motion of the ocean, thanks to an interesting wave power system.
First, though, about those VAWTs. Compared to the pinwheel-style horizontal-axis turbines we're used to seeing, VAWTs have a couple of key advantages, particularly in an offshore wind application. For starters, the heavy generator bit is at the bottom, as opposed to at the top of a gigantic pole that also needs to support a huge spinning fan. So this platform will stay upright by itself, without the need for counterbalances or heavy support structures.
Secondly, they can accept wind from any direction, since they're spinning 360 degrees anyway. So the platform can be oriented parallel with the waves, to best serve its major power producer.
The wave energy generator works in an interesting way, too. The big pluggy-looking thing sticking out of the top is a turbine/generator system, sitting on top of a great big piston. The top of this piston is fixed to the floating platform, and the bottom to the ocean floor.
In between waves, the platform floats downward, and at the bottom of its travel, a valve closes to hold the platform down as the next wave starts to rise. As it does, up to 3 m (10 ft) of this giant float is held underwater, trapping some 600 cubic meters (21,200 cu ft) of air underwater, which desperately wants to rise upward.



