
Breaking News
 The Self-Sufficiency Myth No One Talks About
The Self-Sufficiency Myth No One Talks About
 We Investigated The Maui Fires and The Cover-Up is Worse Than We Thought | Redacted
We Investigated The Maui Fires and The Cover-Up is Worse Than We Thought | Redacted
 The Amish Secret to Keeping Pests Out of Your Garden Forever
The Amish Secret to Keeping Pests Out of Your Garden Forever
 Scott Ritter: Full-Scale War as Iran Attacks All U.S. Targets
Scott Ritter: Full-Scale War as Iran Attacks All U.S. Targets
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Airbus and Toshiba team up to create superconducting aircraft motor
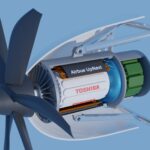
Of all the options for making aircraft emissions-free that doesn't include just turning them all into gliders, hydrogen is the most promising because it combines a relatively high energy density with the ability to reduce emissions to little more than water. However, hydrogen takes up a lot of room for the available energy compared to aviation fuel, and the only practical way to handle it is as a cryogenic liquid cooled to below -253 °C (-423 °F).
In hydrogen-powered aircraft, The idea is that the hydrogen is fed into a fuel cell that generates electricity that either charges battery banks or drives an electric motor directly. However, there's still a weight problem because electric motors powerful enough to be practical for conventional-sized aircraft are very heavy, with a poor power-to-weight ratio.
To overcome this, both Airbus, through its Airbus UpNext subsidiary, and Toshiba, through its Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation energy arm, have been looking at how to use the liquid hydrogen for the fuel cells to cool a cryogenic superconducting electric motor before going to the fuel cell.
When certain materials are cooled below a certain temperature, like that of liquid hydrogen, they become superconducting. In other words, the material's electrical resistance drops almost to zero and can hold an electrical current indefinitely. This allows for much more powerful and efficient magnets at the heart of CAT scanners, particle accelerators, some power transmission networks, and, wait for it, electric motors.
In fact, Airbus claims that a superconducting motor is over three times lighter than a conventional system and has a 97% powertrain efficiency rating. This makes for a lot more power coming out of a much smaller, lighter package – something obviously attractive for use on an aircraft.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

