
Breaking News
 Jake Paul - Trump interview: We cover the Iran war, immigration policies, the assassination...
Jake Paul - Trump interview: We cover the Iran war, immigration policies, the assassination...
 US Attorney Jeanine Pirro just announced activist Judge Boasberg has BLOCKED a Grand Jury...
US Attorney Jeanine Pirro just announced activist Judge Boasberg has BLOCKED a Grand Jury...
 Cost of the Iran War--and Why It Will Fuel Inflation
Cost of the Iran War--and Why It Will Fuel Inflation
 Senator Ted Cruz Says "Christ Is King" Means "I Hate The Jews" & Jews, Not Chris
Senator Ted Cruz Says "Christ Is King" Means "I Hate The Jews" & Jews, Not Chris
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Iron-fortified lumber could be a greener alternative to steel beams
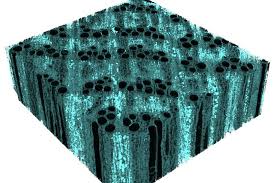
Scientists have now set about addressing that shortcoming, by strengthening wood with added iron.
Led by Asst. Prof. Vivian Merk, a team of researchers at Florida Atlantic University (FAU) started out with cubes of untreated red oak hardwood. Red oak – along with hardwoods like maple, cherry and walnut – is an example of what's known as ring-porous wood. In a nutshell, this means that it utilizes large ring-shaped internal vessels to draw water up from the tree's roots to its leaves.
The scientists proceeded to mix ferric nitrate with potassium hydroxide, creating a hard iron oxide mineral called nanocrystalline ferrihydrite, which occurs naturally in soil and water. Utilizing a vacuum impregnation process, nanoparticles of that ferrihydrite were drawn into the wood and deposited inside of its individual cell walls.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

