
Breaking News
 Widow of killed fire chief not satisfied with Secret Service suspensions...
Widow of killed fire chief not satisfied with Secret Service suspensions...
 Gunman leaves multiple injured at church after shooting cop at Kentucky's Blue Grass Airport
Gunman leaves multiple injured at church after shooting cop at Kentucky's Blue Grass Airport
 One year later: White House highlight Trump's legacy on anniversary of assassination attempt
One year later: White House highlight Trump's legacy on anniversary of assassination attempt
 Arizona homeowner fined by petty HOA for act of kindness during extreme heat
Arizona homeowner fined by petty HOA for act of kindness during extreme heat
Top Tech News
Magic mushrooms may hold the secret to longevity: Psilocybin extends lifespan by 57%...
 Unitree G1 vs Boston Dynamics Atlas vs Optimus Gen 2 Robot– Who Wins?
Unitree G1 vs Boston Dynamics Atlas vs Optimus Gen 2 Robot– Who Wins?
 LFP Battery Fire Safety: What You NEED to Know
LFP Battery Fire Safety: What You NEED to Know
 Final Summer Solar Panel Test: Bifacial Optimization. Save Money w/ These Results!
Final Summer Solar Panel Test: Bifacial Optimization. Save Money w/ These Results!
 MEDICAL MIRACLE IN JAPAN: Paralyzed Man Stands Again After Revolutionary Stem Cell Treatment!
MEDICAL MIRACLE IN JAPAN: Paralyzed Man Stands Again After Revolutionary Stem Cell Treatment!
 Insulator Becomes Conducting Semiconductor And Could Make Superelastic Silicone Solar Panels
Insulator Becomes Conducting Semiconductor And Could Make Superelastic Silicone Solar Panels
 Slate Truck's Under $20,000 Price Tag Just Became A Political Casualty
Slate Truck's Under $20,000 Price Tag Just Became A Political Casualty
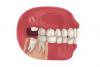 Wisdom Teeth Contain Unique Stem Cell That Can Form Cartilage, Neurons, and Heart Tissue
Wisdom Teeth Contain Unique Stem Cell That Can Form Cartilage, Neurons, and Heart Tissue
 Hay fever breakthrough: 'Molecular shield' blocks allergy trigger at the site
Hay fever breakthrough: 'Molecular shield' blocks allergy trigger at the site
Unibabies: Lab-Grown Sperm And Eggs Just Seven Years Away
Speaking to the Guardian, Prof Katsuhiko Hayashi, a developmental geneticist at the University of Osaka, said rapid progress is being made towards being able to transform adult skin or blood cells into eggs and sperm, a feat of genetic conjury known as in-vitro gametogenesis (IVG).
His own lab is about seven years away from the milestone, he predicts. Other frontrunners include a team at the University of Kyoto and a California-based startup, Conception Biosciences, whose Silicon Valley backers include the OpenAI founder, Sam Altman and whose CEO told the Guardian that growing eggs in the lab "might be the best tool we have to reverse population decline" and could pave the way for human gene editing.
"I feel a bit of pressure. It feels like being in a race," said Hayashi, speaking before his talk at the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology's (ESHRE) annual meeting in Paris this week. "On the other hand, I always try to persuade myself to keep to a scientific sense of value."
If shown to be safe, IVG could pave the way for anyone – regardless of fertility or age – to have biological children. And given that Hayashi's lab previously created mice with two biological fathers, theoretically this could extend to same-sex couples.
"We get emails from [fertility] patients, maybe once a week," said Hayashi. "Some people say": 'I can come to Japan.' So I feel the demand from people."
Matt Krisiloff, Conception's CEO, told the Guardian that lab-grown eggs "could be massive in the future".
"Just the aspect alone of pushing the fertility clock … to potentially allow women to have children at a much older age would be huge," he said. "Outside of social policy, in the long term this technology might be the best tool we have to reverse population decline dynamics due to its potential to significantly expand that family planning window."

 AI Getting Better at Medical Diagnosis
AI Getting Better at Medical Diagnosis

