
Breaking News
 BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
 The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
 Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
 Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
World's blackest material is now world's blackest "spray paint"
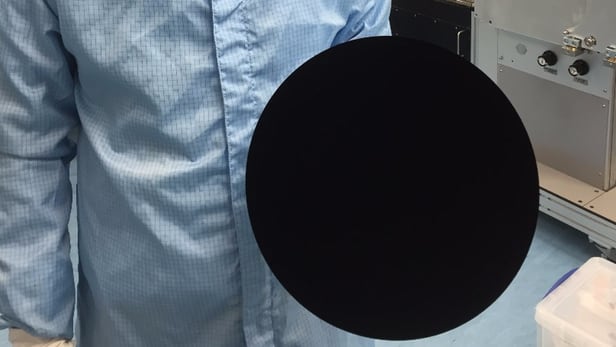
If you're building an ultra-sensitive space telescope, for instance, you want to minimize reflections within that device as much as humanly possible. That's why Surrey NanoSystems released its Vantablack coating two years ago. Now, in order to expand its possible applications, the material is available in a convenient spray-on form.
The conventional form of Vantablack is made up of a forest of light-absorbing carbon nanotubes, and is applied to surfaces via a chemical vapour deposition process. Once in place, it traps 99.965 percent of incoming light – that's enough to make three-dimensional objects which are coated in it appear as two-dimensional voids, across a wide range of viewing angles.
The new version, known as Vantablack S-VIS, is almost as good – it traps 99.8 percent of ultraviolet, visible and infrared light. According to Surrey Nanosystems, that's 17 times less reflective than the super-black paint used in the Hubble telescope.



