
Breaking News
 A Jubilant Lindsey Graham Goes Full NeoCon: "You See this Hat?…The Liberation of Cuba is Upon..
A Jubilant Lindsey Graham Goes Full NeoCon: "You See this Hat?…The Liberation of Cuba is Upon..
 The Economic Impact Of This Horrifying War With Iran Is Not Going To Be Pretty
The Economic Impact Of This Horrifying War With Iran Is Not Going To Be Pretty
 EPISODE 466 (MARCH 5, 2026) | THE HIGHWIRE: VACCINE UPTAKE, LIABILITY, AND ALUMINUM...
EPISODE 466 (MARCH 5, 2026) | THE HIGHWIRE: VACCINE UPTAKE, LIABILITY, AND ALUMINUM...
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Google on track to make quantum computer faster than classical computers within 7 months
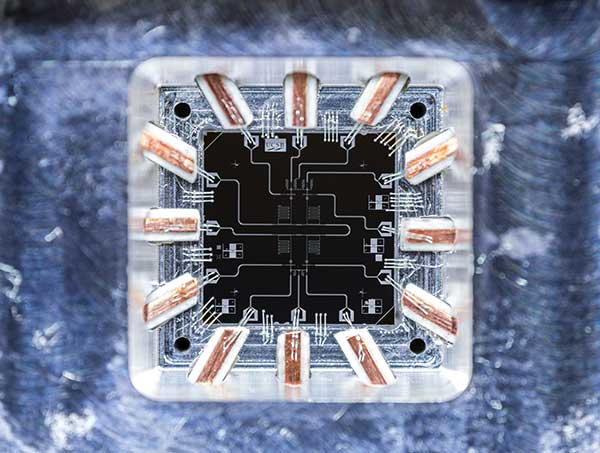
John Martinis, one of Google's quantum computing gurus, laid out Google's "stretch goal": to build and test a 49-qubit ("quantum bit") quantum computer by the end of 2017. This computer will use qubits made of superconducting circuits. Each qubit is prepared in a precise quantum state based on a two-state system. The test will be a milestone in quantum computer technology. In a subsequent presentation, Sergio Boixo, Martinis' colleague at Google, said that a quantum computer with approximately 50 qubits will be capable of certain tasks beyond anything the fastest classical computers can do.
Researchers say that quantum computers promise an exponential increase in speed for a subset of computational chores like prime number factorization or exact simulations of organic molecules. This is because of entanglement: If you prepare entangled qubits, you will be able to manipulate multiple states simultaneously.
New Scientist reports that Google is testing a 20 qubit quantum computer. Alan Ho, an engineer in Google's quantum AI lab, revealed the company's progress at a quantum computing conference in Munich, Germany. His team is currently working with a 20-qubit system that has a "two-qubit fidelity" of 99.5 per cent – a measure of how error-prone the processor is, with a higher rating equating to fewer errors.

 I resigned from OpenAI.
I resigned from OpenAI. 

