
Breaking News
 Jake Paul - Trump interview: We cover the Iran war, immigration policies, the assassination...
Jake Paul - Trump interview: We cover the Iran war, immigration policies, the assassination...
 US Attorney Jeanine Pirro just announced activist Judge Boasberg has BLOCKED a Grand Jury...
US Attorney Jeanine Pirro just announced activist Judge Boasberg has BLOCKED a Grand Jury...
 Cost of the Iran War--and Why It Will Fuel Inflation
Cost of the Iran War--and Why It Will Fuel Inflation
 Senator Ted Cruz Says "Christ Is King" Means "I Hate The Jews" & Jews, Not Chris
Senator Ted Cruz Says "Christ Is King" Means "I Hate The Jews" & Jews, Not Chris
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Lawrence Livermore unlocks 3D printing to smaller than 150 nanometer features
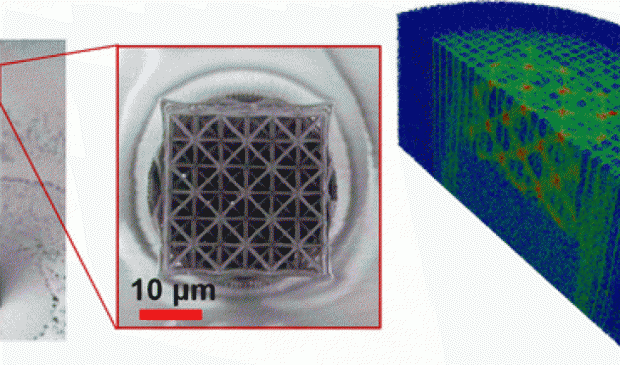
The findings unleashes the potential for X-ray computed tomography (CT) to analyze stress or defects noninvasively in embedded 3D-printed medical devices or implants.
Two-photon lithography typically requires a thin glass slide, a lens and an immersion oil to help the laser light focus to a fine point where curing and printing occurs. It differs from other 3D-printing methods in resolution, because it can produce features smaller than the laser light spot, a scale no other printing process can match. The technique bypasses the usual diffraction limit of other methods because the photoresist material that cures and hardens to create structures — previously a trade secret — simultaneously absorbs two photons instead of one.
LLNL researchers describe cracking the code on resist materials optimized for two-photon lithography and forming 3D microstructures with features less than 150 nanometers. Previous techniques built structures from the ground up, limiting the height of objects because the distance between the glass slide and lens is usually 200 microns or less. By turning the process on its head — putting the resist material directly on the lens and focusing the laser through the resist — researchers can now print objects multiple millimeters in height. Furthermore, researchers were able to tune and increase the amount of X-rays the photopolymer resists could absorb, improving attenuation by more than 10 times over the photoresists commonly used for the technique.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

