
Breaking News
 Why are young women attracted to older men? Men, watch and learn!
Why are young women attracted to older men? Men, watch and learn!
 Voter Fraud Is About To Explode: ITS BLOWING UP IN THEIR FACES thanks to Trump and Tulsi
Voter Fraud Is About To Explode: ITS BLOWING UP IN THEIR FACES thanks to Trump and Tulsi
 Ahead of US-Iran Talks, Netanyahu Tells Cabinet 'Conditions' Could Lead to Regime Change...
Ahead of US-Iran Talks, Netanyahu Tells Cabinet 'Conditions' Could Lead to Regime Change...
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
NASA's X3 ion thruster smashes records in test firings
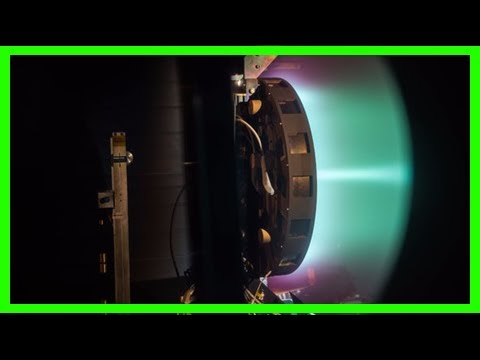
That scenario is now one step closer, as engineers from NASA and the University of Michigan have successfully tested the X3, a thruster designed to get us to Mars. And it's broken several records in the process.
The X3 is one of three Mars engine prototypes currently in development. It is what's known as a Hall thruster, which uses electric and magnetic fields to ionize gases like xenon and expels the ions to produce thrust. The technique is much cleaner, safer and more fuel efficient than traditional chemical rockets, but the trade off is relatively low thrust and acceleration.
"Mars missions are just on the horizon, and we already know that Hall thrusters work well in space," says Alec Gallimore, lead engineer on the X3's development. "They can be optimized either for carrying equipment with minimal energy and propellant over the course of a year or so, or for speed — carrying the crew to Mars much more quickly."



