
Breaking News
 Why are young women attracted to older men? Men, watch and learn!
Why are young women attracted to older men? Men, watch and learn!
 Voter Fraud Is About To Explode: ITS BLOWING UP IN THEIR FACES thanks to Trump and Tulsi
Voter Fraud Is About To Explode: ITS BLOWING UP IN THEIR FACES thanks to Trump and Tulsi
 Ahead of US-Iran Talks, Netanyahu Tells Cabinet 'Conditions' Could Lead to Regime Change...
Ahead of US-Iran Talks, Netanyahu Tells Cabinet 'Conditions' Could Lead to Regime Change...
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Precise control of the properties of plastics
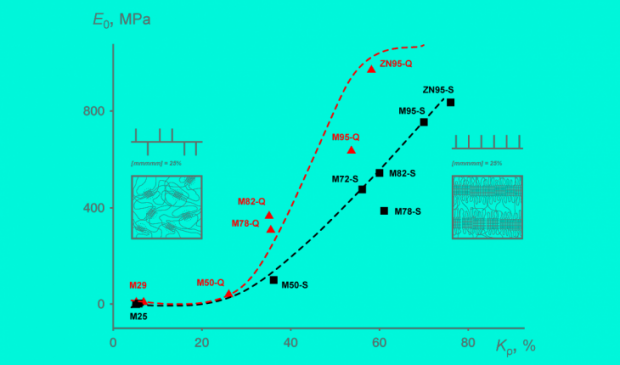
Their new insights make it possible to synthesize a material with predetermined properties, such as elasticity or hardness.
Polypropylene is so ubiquitous one might call it the king of plastics. In terms of production volume, it is second only to polyethylene. By tweaking its molecular structure, polypropylene can be used to manufacture materials with a wide range of features, from elastic bands to high-impact plastic. However, the relationship between the polymer's chemical structure and its mechanical properties was not fully understood.
A polypropylene chain consists of a backbone of carbon atoms with attached hydrogen atoms. Every other carbon atom in the chain has a methyl group attached to it. Two adjacent carbon atoms in the chain with the hydrogen atoms and the methyl group bonded to them constitute a repeating unit called propylene, or propene. The spatial configuration of the macromolecule — the polymer chain — is determined by the mutual orientation of the methyl groups in the chain : If they are all on one side, the molecule is said to be isotactic.



