
Breaking News
 Losing Chickens? Tools Needed for Trapping Poultry Predators
Losing Chickens? Tools Needed for Trapping Poultry Predators
 Metals Tell the Truth About the Economy
Metals Tell the Truth About the Economy
 RFK Jr. baffled over how Trump is alive with diet 'full of poison,'
RFK Jr. baffled over how Trump is alive with diet 'full of poison,'
 Dr. Peter McCullough Responds To Anthony Fauci Criminal Referral
Dr. Peter McCullough Responds To Anthony Fauci Criminal Referral
Top Tech News
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
 US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
 Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
MIT imaging technique sheds light on the brain's electrical activity
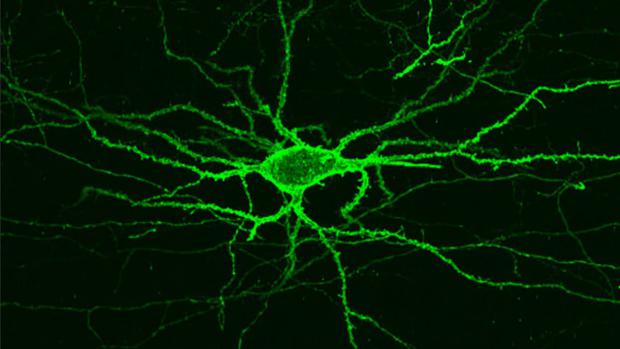
Brain MRIs offer important insight into how our brains work, but they can only produce crude approximations of the areas that are activated by a given stimulus. In order to unravel the minutiae of how neurons communicate and collaborate to form thoughts and feelings, we would need imaging tools with vastly improved resolutions.
Today, far from being able to tackle the 86 billion neurons in the human brain, neuroscientists must settle for studying simple organisms like worms and fish larvae (with neuron counts in the hundreds), relying on slow and cumbersome methods like implanting electrodes into brain tissue to detect electrical signals.
This, however, could soon change. The group of researchers led by Prof. Ed Boyden at MIT has built on previous work to perfect an imaging technique that provides a much fuller picture of the brain's activity. When exposed to red light, a carefully selected fluorescent protein bound to the cellular membrane of neurons reacts to electrical signals by lighting up, to reveal the exact neural path of a thought.

 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this

