
Breaking News
 Grow Unlimited Protein In A Trash Can. No Soil. No Sunlight. The 5 Min Setup.
Grow Unlimited Protein In A Trash Can. No Soil. No Sunlight. The 5 Min Setup.
 Why Amish Gardens Never Have Pests -- The One "Stick" Method Corporations Hate.
Why Amish Gardens Never Have Pests -- The One "Stick" Method Corporations Hate.
 7 MINUTE BUILD | Off-Grid DIY Underground Earthbag Pantry, Root Cellar, and Storm Shelter
7 MINUTE BUILD | Off-Grid DIY Underground Earthbag Pantry, Root Cellar, and Storm Shelter
 Sedentary Adulthood Increases Biological Stress Levels by Middle Age
Sedentary Adulthood Increases Biological Stress Levels by Middle Age
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Roll-to-roll chemical vapor deposition system makes long sheets of high quality graphene
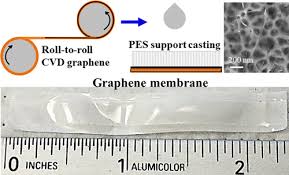
MIT has combined a roll-to-roll approach — a common industrial approach for continuous processing of thin foils — with the common graphene-fabrication technique of chemical vapor deposition, to manufacture high-quality graphene in large quantities and at a high rate.
The system consists of two spools, connected by a conveyor belt that runs through a small furnace. The first spool unfurls a long strip of copper foil, less than 1 centimeter wide. When it enters the furnace, the foil is fed through first one tube and then another, in a "split-zone" design.
While the foil rolls through the first tube, it heats up to a certain ideal temperature, at which point it is ready to roll through the second tube, where the scientists pump in a specified ratio of methane and hydrogen gas, which are deposited onto the heated foil to produce graphene.
"Graphene starts forming in little islands, and then those islands grow together to form a continuous sheet," Hart says. "By the time it's out of the oven, the graphene should be fully covering the foil in one layer, kind of like a continuous bed of pizza."
The researchers found that they were able to feed the foil continuously through the system, producing high-quality graphene at a rate of 5 centimeters per minute. Their longest run lasted almost four hours, during which they produced about 10 meters of continuous graphene.



